Skin Lesions 101: Understanding and Addressing Common Concerns

Welcome to Skin Lesions 101, your go-to resource for understanding and managing common skin issues. Skin lesions can be a cause for concern, but with the right knowledge and guidance, you can navigate through them effectively. Whether you’re dealing with a rash, mole, or other skin abnormalities, this blog aims to provide you with valuable insights and tips for maintaining healthy skin.
What are Skin Lesions?
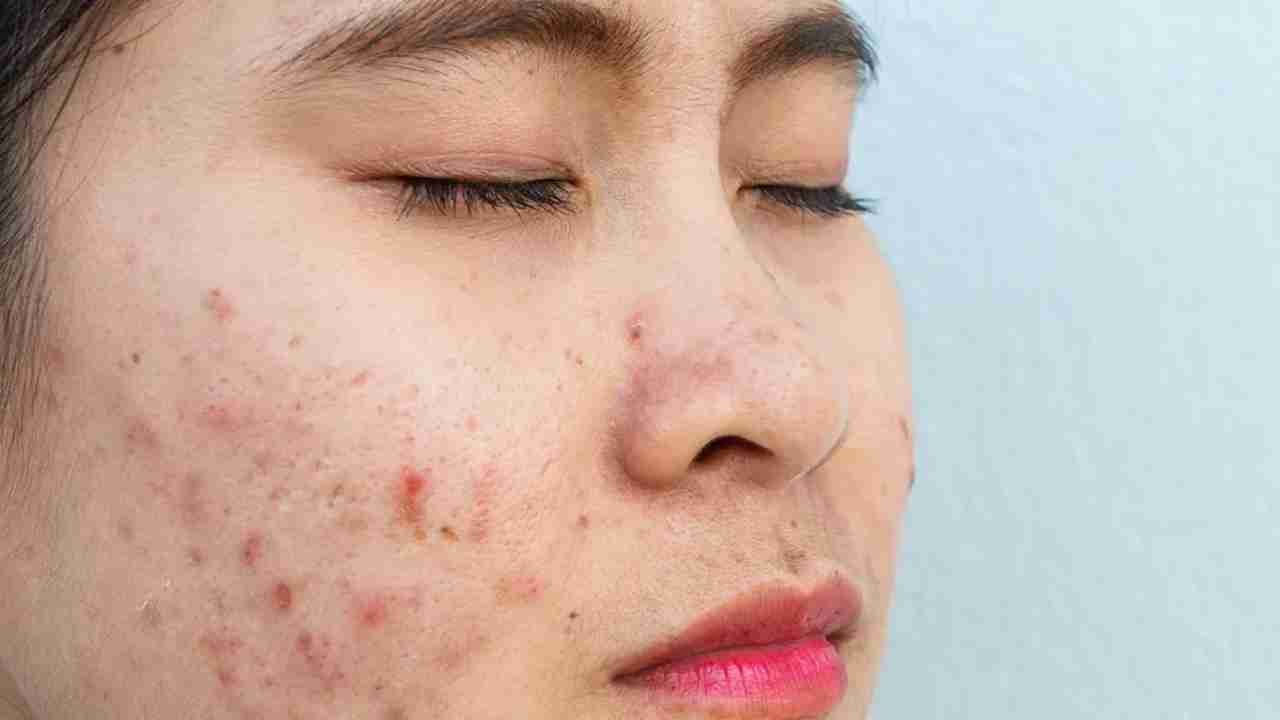
In this section, we’ll define what skin lesions are and discuss the various types, including moles, rashes, bumps, and growths. Understanding the different characteristics of skin lesions is crucial for proper identification and management.
Identifying Common Skin Lesions
Here, we’ll delve into the specifics of different types of skin lesions commonly encountered by individuals. From benign moles to potentially concerning growths, we’ll provide descriptions, images, and tips on how to differentiate between them.
Causes and Risk Factors
What causes skin lesions? This section will explore the various factors that contribute to the development of skin lesions, including genetics, sun exposure, infections, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding the root causes can help you take preventive measures and make informed decisions about your skin health.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Not all skin lesions are cause for immediate concern, but some may warrant medical attention. We’ll discuss red flags to watch out for, such as changes in size, shape, color, and texture of lesions, as well as symptoms like pain, itching, or bleeding. Knowing when to consult a dermatologist is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Tips for Prevention and Care
Prevention is key when it comes to skin health. In this section, we’ll share practical tips for preventing skin lesions, including sun protection measures, proper skincare routines, and lifestyle adjustments. We’ll also discuss how to care for existing lesions to prevent complications and promote healing.
Treatment Options
From topical creams to surgical procedures, there are various treatment options available for managing skin lesions. We’ll explore the different approaches used by dermatologists to address specific types of lesions, emphasizing the importance of personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
Skin Lesions and Mental Health
Living with skin lesions can take a toll on mental well-being, affecting self-esteem and confidence. In this section, we’ll discuss the psychological impact of skin lesions and offer strategies for coping with feelings of anxiety, embarrassment, or self-consciousness. We’ll also highlight the importance of seeking support from healthcare professionals and loved ones.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the common types of skin lesions?
- Skin lesions encompass a wide range of abnormalities, including moles, rashes, bumps, ulcers, and growths. Common examples include acne, eczema, psoriasis, warts, skin tags, and actinic keratoses.
2. How can I differentiate between benign and potentially concerning skin lesions?
- Benign lesions often have regular borders, uniform color, and symmetrical shape. In contrast, concerning lesions may exhibit irregular borders, variation in color, asymmetry, or changes in size, shape, or texture over time.
3. Can I remove skin lesions at home?
- While some benign lesions may respond to home remedies or over-the-counter treatments, it’s essential to exercise caution. Attempting to remove lesions at home without proper guidance can lead to complications, scarring, or delays in diagnosis and treatment of potentially concerning lesions.
4. What are the treatment options for skin lesions?
- Treatment options vary depending on the type, size, and location of the lesion. Common approaches include topical treatments (e.g., creams, ointments), cryotherapy, electrosurgery, excisional surgery, laser therapy, photodynamic therapy, medications, and radiation therapy.
5. Is it necessary to seek medical attention for all skin lesions?
- While not all skin lesions require immediate medical attention, it’s essential to monitor them for any changes or symptoms that may indicate a need for evaluation by a healthcare professional. Red flags include changes in size, shape, color, texture, or symptoms like pain, itching, or bleeding.
6. Are skin lesions always indicative of skin cancer?
- No, most skin lesions are benign and pose no threat to health. However, some lesions, such as certain types of moles or growths, may warrant further evaluation for skin cancer. It’s crucial to consult a dermatologist for proper assessment and diagnosis.
7. How can I protect my skin from developing lesions?
- Practice sun protection measures, including wearing sunscreen, seeking shade, and wearing protective clothing and hats. Maintain a healthy skincare routine, avoid harsh chemicals or irritants, and address underlying health conditions that may predispose you to skin lesions.
8. Can skin lesions be prevented?
- While not all skin lesions can be prevented, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, practicing sun safety, maintaining proper skincare, and avoiding known risk factors can help reduce the likelihood of developing certain types of lesions.
9. What is the long-term outlook for individuals with skin lesions?
- The long-term outlook depends on various factors, including the type and severity of the lesion, response to treatment, and individual health status. Many benign lesions can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, while others may require ongoing monitoring or intervention.
10. When should I schedule a skin check with a dermatologist?
- It’s advisable to schedule a skin check with a dermatologist if you notice any new or changing lesions, have a personal or family history of skin cancer, or have concerns about the health of your skin. Regular skin checks can help detect and manage skin lesions early, improving outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
Register for My Upcoming Masterclass HERE
See You in the Live Masterclass
Sunil Chaudhary stands as a preeminent global Leading digital coach, boasting a diverse clientele hailing from over 50 nations. Renowned for his prowess as an exemplary SEO expert, business automation coach, and landing page authority, Chaudhary also holds the distinction of being esteemed as the finest business coach in India. Beyond technical domains, he imparts invaluable insights into mindset, success, and life skills, thus encompassing a holistic approach to mentorship.