Can Uterine Fibroids Harm Pregnancy? Know Common Symptoms and Treatment
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the uterus that often appear during childbearing years. While many women with fibroids have uncomplicated pregnancies, some may experience complications. Understanding the potential effects of fibroids on pregnancy, recognizing common symptoms, and knowing available treatments is crucial for expectant mothers.
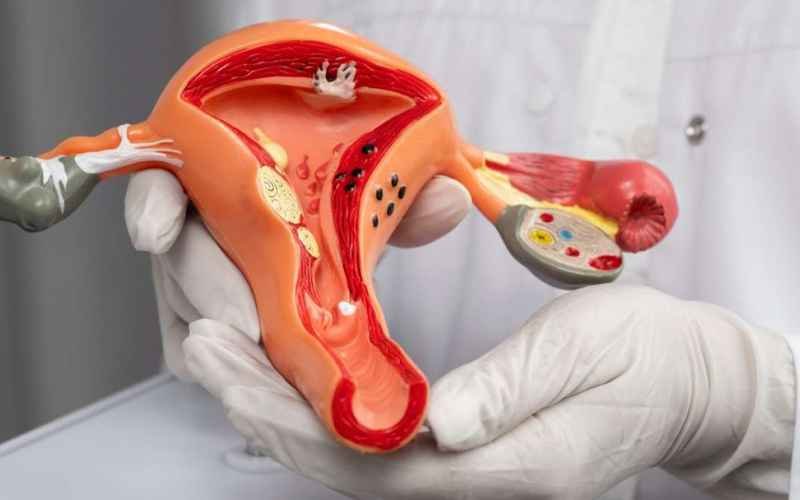
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that originate in the muscular tissue of the uterus, known as the myometrium. These growths are commonly referred to as leiomyomas or myomas. They are typically composed of smooth muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue. While the exact cause of fibroids is not fully understood, several factors such as hormonal imbalances, genetic predisposition, and estrogen and progesterone levels are believed to play a role in their development.
Fibroids can vary significantly in size, shape, and location within the uterus. Some fibroids are so small that they are barely noticeable, while others can grow to be quite large, potentially causing significant distortion of the uterine cavity. In some cases, fibroids can even protrude from the uterus and appear as lumps on the outer surface.
The location of fibroids within the uterus can also vary. Subserosal fibroids grow on the outer surface of the uterus, intramural fibroids develop within the muscular wall of the uterus, and submucosal fibroids grow into the uterine cavity. The symptoms and potential complications associated with fibroids can depend on their size, number, and location.
Despite being called tumors, fibroids are benign, meaning they are not cancerous. However, they can still cause a range of symptoms and complications, including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain or pressure, urinary frequency or urgency, constipation, and infertility. Additionally, fibroids can increase the risk of certain pregnancy complications such as miscarriage, preterm birth, and the need for cesarean delivery.
Diagnosing uterine fibroids typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans. Treatment options for fibroids depend on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, the size and location of the fibroids, and the patient’s age and desire for future fertility. Treatment may include watchful waiting with regular monitoring, medication to control symptoms, minimally invasive procedures to shrink or remove fibroids, or surgery such as hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) in severe cases.
Can Fibroids Harm Pregnancy?
Uterine fibroids, although typically benign, can indeed pose risks and complications during pregnancy, depending on their size, location, and impact on the uterus and surrounding structures. Here’s an elaboration on how fibroids can potentially harm pregnancy:
- Infertility: Large fibroids can sometimes interfere with fertility by obstructing the fallopian tubes or distorting the uterine cavity. They can create mechanical barriers that prevent sperm from reaching the egg or hinder the implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterine lining. Additionally, fibroids may disrupt the normal functioning of the uterus, affecting its ability to support a developing embryo.
- Miscarriage: Fibroids, especially when they distort the shape of the uterine cavity or disrupt blood flow to the placenta, can increase the risk of miscarriage. The presence of fibroids may lead to implantation failure or compromise the blood supply to the developing fetus, resulting in miscarriage during early pregnancy stages. Additionally, fibroids can contribute to complications such as placental abruption, where the placenta separates from the uterine wall prematurely, leading to fetal distress and potential loss.
- Preterm Birth: Fibroids are associated with an increased risk of preterm labor and delivery. The presence of fibroids in the uterus can lead to uterine irritability, which may trigger contractions and premature labor. Additionally, fibroids can cause the uterus to stretch prematurely or disrupt its ability to hold the fetus to term, resulting in preterm birth. Babies born prematurely are at higher risk of various health complications, including respiratory distress syndrome, developmental delays, and long-term disabilities.
- Cesarean Delivery: Women with fibroids, particularly those located near the cervix or blocking the birth canal, may require a cesarean section (C-section) for delivery. Fibroids can obstruct the natural passage for the baby to pass through during vaginal delivery, increasing the likelihood of complications such as obstructed labor or fetal distress. A C-section may be necessary to ensure the safety of both the mother and the baby.
- Management and Monitoring: Pregnant women with fibroids typically require close monitoring throughout their pregnancy to assess the size and location of the fibroids and monitor any potential complications. Management strategies may include regular ultrasound examinations, monitoring fetal growth and well-being, and addressing any symptoms or complications that arise during pregnancy. In some cases, medical or surgical interventions may be necessary to manage symptoms or reduce the risk of pregnancy complications associated with fibroids.
Common Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids can manifest with a variety of symptoms, although some women may not experience any noticeable signs. Understanding the common symptoms associated with fibroids is crucial for early detection and proper management. Here’s an elaboration on the typical symptoms of uterine fibroids:
1. Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Menorrhagia):
One of the most common symptoms of uterine fibroids is heavy menstrual bleeding. Women with fibroids often experience prolonged or excessively heavy periods, which can lead to significant blood loss and result in anemia. Menorrhagia can interfere with daily activities and quality of life, causing fatigue, weakness, and difficulty performing routine tasks.
2. Pelvic Pain and Discomfort:
Fibroids can cause pelvic pain or discomfort, which may range from mild to severe. Women with fibroids may experience pelvic pressure, aching, or cramping, particularly during menstruation or sexual intercourse. The pain can be localized to the lower abdomen or pelvis and may radiate to the lower back or thighs. The severity and frequency of pelvic pain can vary depending on the size, number, and location of the fibroids.
3. Frequent Urination:
Large fibroids can exert pressure on the bladder, leading to urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, urgency, or difficulty emptying the bladder completely. Women with fibroids may find themselves needing to urinate more frequently than usual, even waking up at night to urinate (nocturia). In some cases, fibroids can also cause urinary retention or urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to incomplete emptying of the bladder.
4. Constipation and Bowel Changes:
Fibroids located near the rectum or exerting pressure on the intestines can cause constipation or difficulty passing stools. Women with fibroids may experience infrequent bowel movements, straining during bowel movements, or a sensation of incomplete evacuation. Fibroids can also lead to other bowel symptoms such as bloating, abdominal discomfort, or changes in bowel habits.
5. Abdominal Swelling and Enlargement:
Enlarged fibroids can cause the abdomen to protrude or swell, resembling a pregnant belly. Abdominal swelling due to fibroids is often progressive and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as pelvic pain, pressure, or urinary symptoms. The extent of abdominal swelling can vary depending on the size and number of fibroids present in the uterus.
Treatment Options During Pregnancy
Treatment options for uterine fibroids during pregnancy are typically approached with caution due to the potential risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. The management plan depends on several factors, including the size and location of the fibroids, the severity of symptoms, and the stage of pregnancy. Here’s an elaboration on the treatment options available:
1. Monitoring:
In many cases, uterine fibroids discovered during pregnancy may not require immediate intervention. Instead, healthcare providers may opt for regular monitoring through ultrasound examinations to assess the growth and impact of the fibroids on the pregnancy. Monitoring allows healthcare providers to track any changes in the size or position of the fibroids and evaluate their potential effect on the mother and fetus.
2. Pain Management:
For women experiencing discomfort or pain associated with fibroids during pregnancy, over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) may be recommended to alleviate symptoms. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and aspirin are generally avoided during pregnancy due to potential risks to the fetus.
3. Medical Intervention:
In rare cases where fibroids cause severe symptoms or complications during pregnancy, medical treatment may be necessary. However, treatment options are limited during pregnancy due to potential risks to the fetus. Hormonal medications, such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, may be considered to temporarily shrink fibroids and alleviate symptoms. These medications work by suppressing ovarian function and reducing estrogen levels, which can lead to fibroid shrinkage. However, their use during pregnancy is generally avoided due to potential adverse effects on fetal development.
4. Postpartum Management:
After delivery, women with uterine fibroids may require ongoing management to address any persistent symptoms or complications. Treatment options may include medication to control symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding or pelvic pain. Hormone therapy, such as hormonal contraceptives or progestin-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs), may be considered to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce the growth of fibroids. In some cases, surgical interventions such as myomectomy (removal of fibroids) or hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be recommended if fibroids continue to cause significant problems or if future pregnancies are not desired.
Final Thoughts
While uterine fibroids can potentially complicate pregnancy, many women with fibroids have successful pregnancies with proper monitoring and medical care. If you’re pregnant and have fibroids or suspect you might, it’s essential to discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider. By working together, you can develop a plan to manage fibroids and ensure the best possible outcome for you and your baby.
Top 20 frequently asked questions (FAQs) about uterine fibroids and their potential impact on pregnancy
- What are uterine fibroids?
- Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in the uterus, often during childbearing years.
- Can uterine fibroids affect pregnancy?
- Yes, depending on their size and location, fibroids can pose risks and complications during pregnancy.
- What are the common symptoms of uterine fibroids?
- Common symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, frequent urination, constipation, and abdominal swelling.
- Can uterine fibroids cause infertility?
- Large fibroids can obstruct fallopian tubes or interfere with embryo implantation, potentially leading to infertility.
- Do fibroids increase the risk of miscarriage?
- Fibroids may increase the risk of miscarriage, especially if they distort the uterine cavity or disrupt blood flow to the placenta.
- Can fibroids lead to preterm birth?
- Yes, fibroids can trigger preterm labor or premature rupture of membranes, increasing the risk of preterm birth.
- Do all women with fibroids require treatment during pregnancy?
- No, many women with fibroids may not require treatment beyond regular monitoring to assess their impact on pregnancy.
- How are fibroids diagnosed during pregnancy?
- Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as ultrasound.
- What is the recommended treatment for fibroids during pregnancy?
- Treatment depends on factors like fibroid size, location, and symptoms, and may include monitoring, pain management, or medical intervention if necessary.
- Are fibroids typically removed during pregnancy?
- Removal of fibroids during pregnancy is rare and usually avoided due to potential risks to the fetus.
- Can fibroids cause complications during delivery?
- Fibroids can increase the likelihood of cesarean delivery, especially if they block the birth canal or pose other risks.
- Can fibroids cause problems during postpartum recovery?
- Fibroids may continue to cause symptoms after delivery, requiring postpartum management with medication or surgical intervention if necessary.
- Do all women with fibroids experience symptoms during pregnancy?
- No, some women with fibroids may remain asymptomatic during pregnancy.
- Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage fibroids during pregnancy?
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, may help alleviate symptoms associated with fibroids.
- Are there any medications that can safely treat fibroids during pregnancy?
- Limited options are available for medication during pregnancy, and any treatment must be carefully evaluated for potential risks to the fetus.
- Can fibroids affect the growth and development of the fetus?
- Large fibroids may exert pressure on the uterus, potentially impacting fetal growth and positioning.
- Can fibroids cause complications in multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, etc.)?
- Multiple pregnancies can increase the risk of complications associated with fibroids, such as preterm birth or cesarean delivery.
- Can fibroids increase the risk of postpartum hemorrhage?
- Fibroids may increase the risk of postpartum hemorrhage due to their impact on uterine tone and contraction.
- Are fibroids associated with an increased risk of other pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia?
- While not directly linked to preeclampsia, fibroids can contribute to other complications such as preterm birth or placental abruption.
- Is it possible for fibroids to shrink or resolve on their own after pregnancy?
- In some cases, fibroids may shrink or regress in size after pregnancy, especially if hormone levels return to normal. However, this is not guaranteed for all women.
These FAQs cover essential aspects of uterine fibroids, their impact on pregnancy, common symptoms, and available treatments. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and management of fibroids during pregnancy.
Register for My Upcoming Masterclass HERE
See You in the Live Masterclass
Sunil Chaudhary stands as a preeminent global Leading digital coach, boasting a diverse clientele hailing from over 50 nations. Renowned for his prowess as an exemplary SEO expert, business automation coach, and landing page authority, Chaudhary also holds the distinction of being esteemed as the finest business coach in India. Beyond technical domains, he imparts invaluable insights into mindset, success, and life skills, thus encompassing a holistic approach to mentorship.










