How to Get Pregnant with Endometriosis Naturally?
March 27, 2025

Ectopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
May 4, 2024

Nurturing Life: A Journey through Pregnancy
May 4, 2024

Pregnancy Signs and Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide
May 4, 2024

Can Uterine Fibroids Harm Pregnancy? Know Common Symptoms and Treatment
April 8, 2024
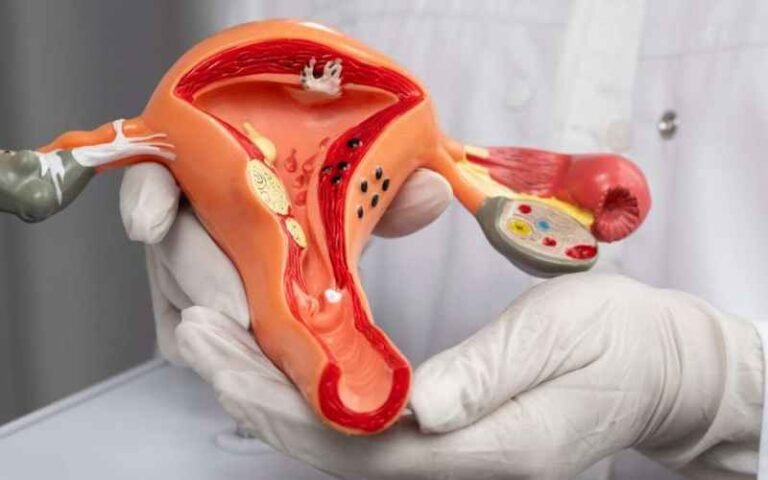
Navigating Rheumatoid Arthritis and Preeclampsia During Pregnancy
March 21, 2024

What is Endometriosis? Know symptoms, treatments and surgical options for chronic pelvic pain
March 16, 2024

Blossoming Beginnings: Understanding Pregnancy Symptoms
March 7, 2024
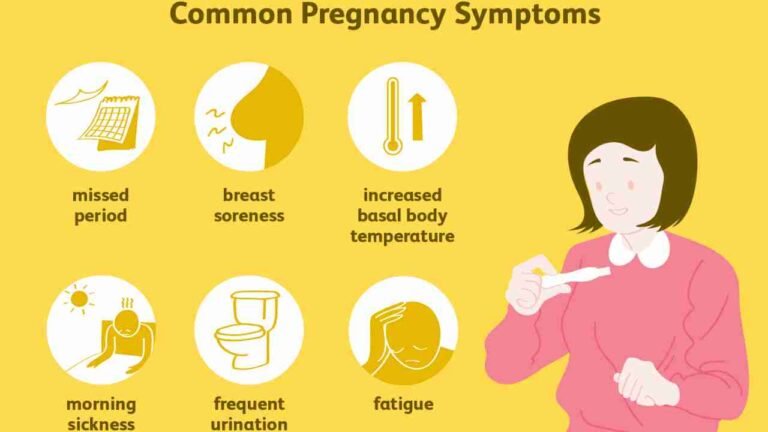
Blossoming Bumps: Your Guide to Pregnancy in India
March 7, 2024










