Knee strength is crucial for overall mobility and stability in our daily activities. Whether you’re an athlete looking to enhance performance or someone recovering from an injury, incorporating targeted exercises into your routine can make a significant difference. In this blog post, we’ll explore five effective exercises ranging from squats to hamstring curls that can help strengthen your knees and promote better joint health.
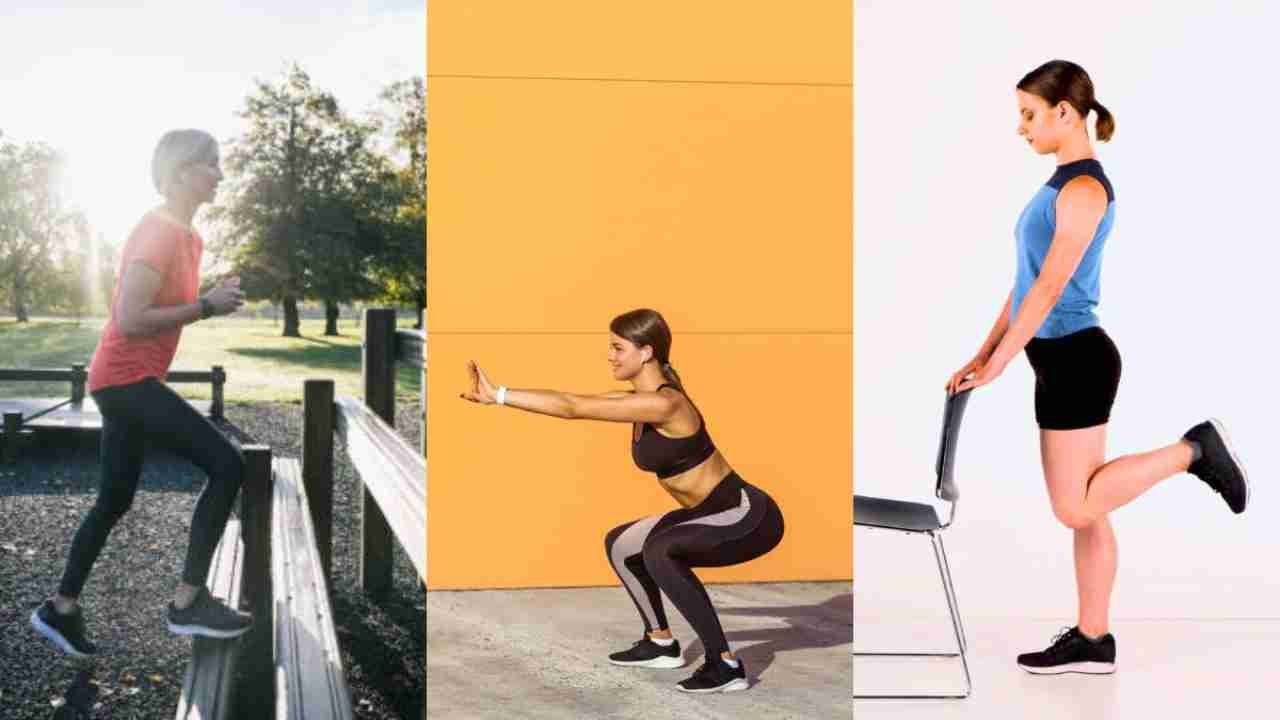
1. Squats: Squats are a fundamental compound exercise that engages multiple muscle groups, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. Performing squats with proper form not only strengthens the muscles around the knee but also improves overall lower body strength and stability. Start with bodyweight squats and gradually progress to weighted squats as you build strength.
Squats stand as one of the cornerstone exercises in any fitness regimen, and for good reason. They are a compound movement, meaning they engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making them incredibly efficient for building strength and muscle mass. When performed correctly, squats primarily target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, but they also engage the core, lower back, and stabilizing muscles throughout the body.
Muscle Engagement:
- Quadriceps: As you lower into the squat position, your quadriceps muscles work to extend the knee joint, allowing you to lower your body towards the ground.
- Hamstrings: Simultaneously, your hamstrings play a crucial role in controlling the descent and providing stability to the knee joint. They work eccentrically to control the lowering phase of the squat.
- Glutes: The gluteus maximus, the largest muscle in the body, is heavily engaged during squats, particularly during the ascent phase. It’s responsible for hip extension, driving your body back up to a standing position.
Benefits for Knee Strength:
- Stabilization: Squats require significant stabilization of the knee joint throughout the movement, helping to strengthen the ligaments and tendons surrounding the knee.
- Joint Integrity: By strengthening the muscles around the knee, squats can help improve joint integrity and reduce the risk of injuries such as strains or tears.
- Functional Movement: Squats mimic movements that we perform in everyday life, such as bending down to pick something up or standing up from a seated position. By strengthening the muscles involved in these movements, squats can improve overall functional capacity and reduce the risk of knee-related issues in daily activities.
Progression: It’s essential to start with bodyweight squats to master the movement pattern and ensure proper form. Focus on maintaining a neutral spine, keeping your chest up, and tracking your knees over your toes. As you become more comfortable, gradually increase the difficulty by adding resistance through dumbbells, barbells, or kettlebells. Progression can also involve variations such as front squats, goblet squats, or Bulgarian split squats to target different muscle groups and challenge your body in new ways.
Conclusion: Incorporating squats into your workout routine not only strengthens the muscles around the knee joint but also contributes to overall lower body strength and stability. Start with bodyweight squats, focus on proper form, and gradually progress to more challenging variations as you build strength and confidence. With consistent practice, squats can become a foundational exercise for improving knee health and enhancing functional movement patterns in your daily life.
2. Lunges: Lunges are another excellent exercise for targeting the muscles around the knee joint while also improving balance and coordination. Front lunges, reverse lunges, and lateral lunges are variations that target different muscle groups in the lower body. Focus on maintaining proper alignment and control throughout the movement to maximize effectiveness and minimize the risk of injury.
Lunges are a versatile and effective exercise for targeting the muscles around the knee joint, while also providing numerous additional benefits such as improved balance, coordination, and unilateral strength development. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced athlete, incorporating lunges into your workout routine can help enhance lower body strength and stability.
Muscle Engagement:
- Quadriceps: Lunges primarily target the quadriceps, particularly during the descending phase when the knee flexes. The quadriceps work to stabilize the knee joint and provide the necessary strength to push back up to the starting position.
- Hamstrings: Similar to squats, lunges engage the hamstrings to control the descent and provide stability to the knee joint. The hamstrings work eccentrically to lower the body and concentrically to push back up.
- Glutes: Lunges heavily recruit the glutes, especially during the ascent phase when the hip extends. The gluteus maximus is responsible for driving the body back up to the starting position.
Variations and Targeted Muscle Groups:
- Front Lunges: Front lunges primarily target the quadriceps, but they also engage the glutes and hamstrings to a lesser extent. This variation emphasizes forward movement and requires stability and balance.
- Reverse Lunges: Reverse lunges place more emphasis on the hamstrings and glutes while still targeting the quadriceps. The movement involves stepping backward, which can help improve coordination and balance.
- Lateral Lunges: Lateral lunges target the adductor muscles of the inner thigh, as well as the glutes and quadriceps. This variation promotes side-to-side movement and challenges stability in a different plane of motion.
Focus on Proper Form: Maintaining proper alignment and control throughout the movement is crucial for maximizing effectiveness and reducing the risk of injury during lunges. Key points to remember include:
- Keep your torso upright and shoulders back to maintain a neutral spine.
- Ensure your front knee stays aligned with your ankle and does not extend past your toes to prevent undue stress on the knee joint.
- Lower your body until your back knee hovers just above the ground, aiming for a 90-degree angle at both knees.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your body and maintain balance throughout the movement.
Conclusion: Lunges offer a comprehensive lower body workout that targets the muscles around the knee joint while also improving balance, coordination, and unilateral strength. Incorporating variations such as front lunges, reverse lunges, and lateral lunges into your routine can help target different muscle groups and enhance overall lower body strength and stability. Focus on proper form and control to maximize effectiveness and minimize the risk of injury, and enjoy the benefits of stronger, more resilient knees.
3. Leg Press: The leg press machine is a safe and effective way to strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes with controlled resistance. Adjust the machine to your comfort level and gradually increase the weight as you progress. Keep your feet flat on the platform and maintain a stable lower back position throughout the movement to protect your knees and maximize muscle engagement.
The leg press machine is a staple in many gym settings, offering a controlled and effective way to strengthen the muscles of the lower body, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. While squats and lunges are compound movements that engage multiple muscle groups, the leg press isolates the lower body muscles, making it an excellent option for targeting specific areas with controlled resistance.
Safe and Effective Strength Building:
- Quadriceps: The leg press primarily targets the quadriceps, the muscles on the front of the thigh. As you push the weight away from your body, the quadriceps contract to extend the knee joint, effectively working to straighten your legs.
- Hamstrings: While not as heavily engaged as in squats or lunges, the hamstrings play a supporting role in the leg press movement, helping to stabilize the knee joint and control the descent of the weight.
- Glutes: The gluteal muscles also contribute to the leg press movement, particularly during the pushing phase when the hips extend. This engagement helps to provide power and stability throughout the exercise.
Adjustable Resistance and Progression: One of the advantages of the leg press machine is its adjustable resistance, allowing users to customize the weight to their individual strength levels. Beginners can start with a lighter weight and gradually increase the resistance as they build strength and confidence. It’s essential to choose a weight that challenges you without compromising proper form or risking injury.
Proper Form for Maximum Benefit: Maintaining proper form is key to maximizing the effectiveness of the leg press exercise while minimizing the risk of injury:
- Foot Placement: Keep your feet flat on the platform, with your heels positioned shoulder-width apart. This stance helps distribute the load evenly and minimizes stress on the knees.
- Back Position: Maintain a stable lower back position throughout the movement by keeping your spine neutral and avoiding excessive arching or rounding. Press your lower back firmly against the backrest for support.
- Range of Motion: Lower the weight until your knees are bent at approximately 90 degrees, ensuring a full range of motion without locking out the knees at the top of the movement.
- Controlled Movement: Focus on controlled, smooth movements, avoiding sudden jerks or bouncing of the weight. This helps to maintain tension on the muscles and reduces the risk of strain or injury.
Conclusion: The leg press machine offers a safe and effective way to strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes with controlled resistance. By adjusting the machine to your comfort level and focusing on proper form, you can effectively target these muscle groups while minimizing the risk of injury. Incorporate the leg press into your lower body workout routine to build strength, improve muscle definition, and support overall lower body function.
4. Hamstring Curls: Hamstring curls specifically target the muscles on the back of the thigh, which play a crucial role in supporting the knee joint. Whether using a machine or resistance bands, focus on squeezing your hamstrings as you curl the weight or pull the bands towards your glutes. Slow and controlled movements are key to effectively strengthen the hamstrings while minimizing strain on the knees.
Hamstring curls are a targeted exercise designed to isolate and strengthen the muscles on the back of the thigh, known as the hamstrings. These muscles are crucial for supporting the knee joint, stabilizing the leg during movement, and preventing injury. Incorporating hamstring curls into your workout routine can help improve knee stability, enhance athletic performance, and reduce the risk of knee-related issues.
Targeted Muscle Engagement:
- Hamstrings: Hamstring curls primarily target the three muscles that make up the hamstring group: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. As you curl the weight or resistance band towards your glutes, these muscles contract concentrically to flex the knee joint, bringing the heel towards the buttocks.
- Stabilizing Muscles: In addition to the hamstrings, other muscles in the lower body, such as the calves and glutes, also contribute to the movement to provide stability and control.
Machine vs. Resistance Bands: Hamstring curls can be performed using either a dedicated machine or resistance bands, both of which offer effective ways to target the hamstrings:
- Machine: Utilizing a hamstring curl machine provides a guided and controlled range of motion. Adjust the machine to your body size and comfort level, ensuring proper alignment of the joints. Select an appropriate weight that allows you to perform the exercise with proper form while challenging your muscles.
- Resistance Bands: Resistance bands offer a portable and versatile alternative to machines. Secure one end of the band to a stable anchor point and loop the other end around your ankle. Perform the curling motion against the resistance of the band, focusing on maintaining tension in the hamstrings throughout the movement.
Focus on Technique and Control: To maximize the effectiveness of hamstring curls and minimize strain on the knees, it’s essential to prioritize proper technique and control:
- Mind-Muscle Connection: Focus on consciously contracting and squeezing the hamstrings throughout the exercise to ensure optimal muscle engagement.
- Range of Motion: Aim for a full range of motion while maintaining control. Avoid swinging or using momentum to lift the weight, as this can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise and increase the risk of injury.
- Slow and Controlled Movements: Perform hamstring curls with a slow and controlled tempo, emphasizing the eccentric (lowering) phase of the movement. This helps to strengthen the muscles throughout their entire range of motion and reduces the likelihood of overloading the knees.
Conclusion: Incorporating hamstring curls into your workout routine is an effective way to specifically target the muscles on the back of the thigh, which play a vital role in supporting the knee joint. Whether using a machine or resistance bands, focus on proper technique, controlled movements, and maintaining tension in the hamstrings to strengthen these muscles while minimizing strain on the knees. By including hamstring curls in your lower body training regimen, you can improve knee stability, enhance athletic performance, and reduce the risk of injury.
5. Step-Ups: Step-ups are a functional exercise that mimics daily movements like climbing stairs, making them excellent for improving knee strength and stability in real-life scenarios. Use a sturdy bench or step, and step up with one foot followed by the other before stepping back down. Focus on maintaining proper alignment and controlling the movement to avoid unnecessary stress on the knees.
Step-ups are a functional and practical exercise that replicates everyday movements such as climbing stairs or stepping up onto a curb. They are highly effective for improving knee strength and stability while engaging multiple muscle groups in the lower body and core. Incorporating step-ups into your workout routine can enhance overall lower body strength, balance, and coordination, translating to improved performance in daily activities and sports.
Functional Movement Simulation:
- Real-Life Application: Step-ups closely mimic movements we perform in daily life, such as climbing stairs or stepping up onto elevated surfaces. By training these movements in the gym, we can improve our ability to navigate stairs or uneven terrain with greater ease and efficiency.
- Sport-Specific Training: Step-ups are also beneficial for athletes involved in sports that require explosive lower body power, such as basketball or soccer. The dynamic nature of the exercise helps develop strength and coordination that translates directly to athletic performance.
Muscle Engagement:
- Quadriceps: Step-ups primarily target the quadriceps, the muscles on the front of the thigh, as they work to extend the knee joint and lift the body up onto the step.
- Glutes: The gluteal muscles are heavily engaged during step-ups, particularly during the pushing phase when the hips extend. This engagement helps provide power and stability throughout the movement.
- Hamstrings: While not as actively engaged as in some other exercises, the hamstrings play a supporting role in step-ups, assisting with hip extension and knee stabilization.
- Calves: The calf muscles also contribute to the movement, particularly during the final push-off phase when lifting the body onto the step.
Proper Form and Technique:
- Sturdy Surface: Use a sturdy bench, box, or step platform that can support your weight and provide a stable surface for stepping up.
- Foot Placement: Step onto the platform with one foot, ensuring that your entire foot is securely planted and centered on the step. Avoid allowing the heel to hang off the edge.
- Controlled Movement: Focus on a controlled and deliberate movement pattern, avoiding bouncing or jerking motions. Use the muscles of the lower body to lift your body weight onto the step, rather than relying on momentum.
- Alignment: Maintain proper alignment throughout the movement, keeping your knees tracking in line with your toes and avoiding excessive inward or outward movement. Engage your core muscles to stabilize your torso and prevent excessive leaning or swaying.
Progression and Variation: To continue challenging yourself and further improve knee strength and stability, you can incorporate variations such as:
- Holding dumbbells or kettlebells in each hand to increase resistance.
- Performing step-ups with a higher step or platform to increase the range of motion and difficulty.
- Adding a balance challenge by performing step-ups on an unstable surface such as a Bosu ball or foam pad.
Conclusion: Step-ups are a functional and versatile exercise that effectively improves knee strength and stability while mimicking everyday movements like climbing stairs. By focusing on proper form, controlled movements, and gradual progression, you can strengthen the muscles of the lower body and core, enhance balance and coordination, and improve performance in daily activities and sports. Incorporate step-ups into your workout routine to reap the benefits of this highly functional exercise.
Register for My Upcoming Masterclass HERE
See You in the Live Masterclass
Sunil Chaudhary stands as a preeminent global Leading digital coach, boasting a diverse clientele hailing from over 50 nations. Renowned for his prowess as an exemplary SEO expert, business automation coach, and landing page authority, Chaudhary also holds the distinction of being esteemed as the finest business coach in India. Beyond technical domains, he imparts invaluable insights into mindset, success, and life skills, thus encompassing a holistic approach to mentorship.












