Cholesterol is a word we hear often, especially when it comes to heart health. But many people do not fully understand what cholesterol is, why it matters, and when medication may be needed to control it. In simple terms, cholesterol is a type of fat found in your blood. While the body needs some cholesterol to build healthy cells, too much “bad” cholesterol can cause serious problems like heart disease and stroke. Managing cholesterol well is essential for a long, healthy life. In this blog, we will explore what are the top 5 cholesterol medications, how they work, and why they may be important for you or your loved ones. With clear, easy language and expert guidance, you will gain confidence to make better health decisions and take charge of your heart wellness journey.
What are the Top 5 Cholesterol Medications
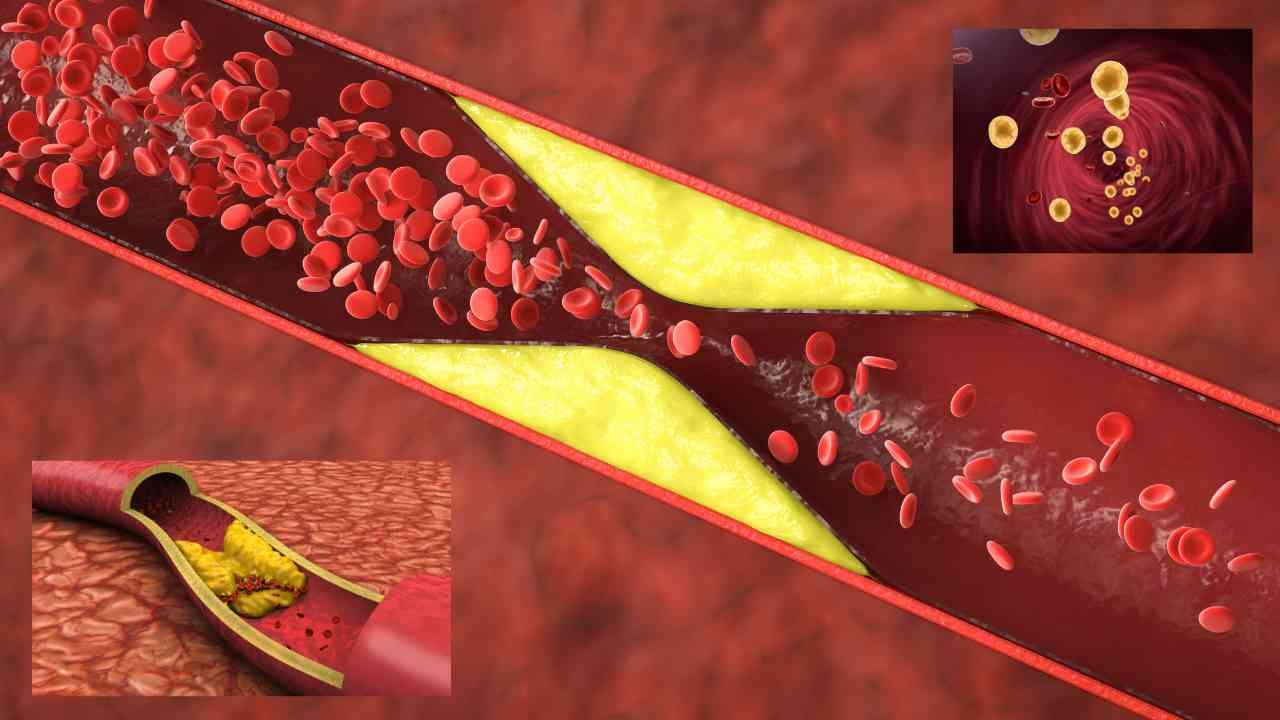
Understanding Cholesterol and Why Medications Matter
Cholesterol is a type of fat that is naturally present in your body and also comes from the food you eat. It plays an important role in building cells, producing hormones, and digesting food. However, not all cholesterol is the same. There are two main types you need to know about—low-density lipoprotein (LDL), often called “bad cholesterol,” and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), known as “good cholesterol.”
What Is LDL and HDL Cholesterol?
LDL cholesterol can build up inside your arteries, forming thick, hard deposits called plaques. These plaques can narrow your arteries and make it harder for blood to flow through. Over time, this can cause serious heart problems such as heart attacks or strokes. This is why LDL is called “bad.”
On the other hand, HDL cholesterol helps remove LDL from your blood by carrying it back to your liver where it is broken down and removed. Higher HDL levels are good because they protect your heart.
Why Is High Cholesterol Dangerous?
When the balance between LDL and HDL is off, and your LDL levels become too high, it increases your risk of cardiovascular diseases. The buildup of plaques inside your arteries not only reduces blood flow but can cause clot formation. This can block blood flow completely resulting in a heart attack or stroke, which can be life-threatening.
Many people with high cholesterol do not have symptoms until they face these severe health events. That’s why managing cholesterol levels proactively is very important.
Lifestyle Versus Medication: When Do You Need Medicines?
Doctors usually recommend lifestyle changes as the first step. This includes eating a healthy diet low in saturated fat and trans fats, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol. These steps can effectively lower cholesterol for many individuals.
However, for some people, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough. This can be due to genetic reasons, existing heart conditions, diabetes, or very high cholesterol levels. In these cases, medication becomes necessary to bring cholesterol to a safe level and reduce health risks.
How Do Cholesterol Medications Work?
Cholesterol medications are designed to lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol, or reduce triglycerides (another type of fat in your blood). Different medicines work in different ways—some reduce the production of cholesterol in the liver, others block absorption from food, and some help your body remove cholesterol more efficiently.
Importance of Expert Medical Advice and Regular Monitoring
Before starting on any medication, it is crucial to have a proper diagnosis and advice from a qualified doctor. They will look at your overall health, family history, and other risk factors to decide if medication is needed and which medication suits you best.
Once on medication, regular monitoring through blood tests is essential to track your cholesterol levels and adjust the treatment if necessary. This helps achieve the best results while minimizing side effects.
Statins – The Cornerstone of Cholesterol Treatment
When it comes to cholesterol medications, statins are the most widely prescribed and trusted by doctors worldwide. They are considered the first line of defense against high LDL cholesterol, often called “bad cholesterol.” Statins have been thoroughly studied and have helped millions of people reduce their risk of heart disease and stroke.
What Are Statins and How Do They Work?
Statins work by blocking an enzyme in the liver that is responsible for making cholesterol. This enzyme, called HMG-CoA reductase, helps the liver produce cholesterol. By blocking this enzyme, statins reduce the amount of cholesterol your liver makes. This leads to lower LDL cholesterol in your blood.
Lower LDL means less cholesterol building up in your arteries. This helps prevent plaque formation, reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems.
Common Types of Statins
There are several statins available, some of the most common include:
Atorvastatin (brand name Lipitor): One of the most prescribed statins, known for effectively lowering LDL cholesterol and improving heart health.
Simvastatin (Zocor): Often used for moderate LDL reduction, suitable for many patients.
Rosuvastatin (Crestor): A powerful statin for those needing greater cholesterol lowering.
Your doctor will help decide which statin and what dose is right for you, based on your cholesterol levels, risk factors, and overall health.
Benefits of Statins
Statins don’t just lower cholesterol; they also:
Stabilize plaques in arteries, making them less likely to break and cause clots.
Reduce inflammation in blood vessels.
Lower the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Help people with or without existing heart disease manage their risks effectively.
Typical Dosage and How to Take Statins
Statins usually come in pill form and are often taken once daily. Many doctors recommend taking statins in the evening because our body produces more cholesterol at night. However, some modern statins can be taken at any time.
The dosage depends on your specific needs. Your healthcare provider will start you on a dose and adjust it if needed depending on your response and any side effects.
Common Side Effects and Myths
Like all medicines, statins can have side effects, but most people tolerate them well. Some common side effects include:
Muscle pain or weakness
Digestive problems (nausea, constipation)
Mild increase in blood sugar levels
Most side effects are mild and improve with time or switching doses. Serious side effects are very rare.
Myths about statins: Some worry about liver damage or memory loss, but scientific studies show these are uncommon. Always discuss your concerns with your doctor before stopping medication.
Managing Concerns and Staying Committed
It is natural to worry about taking medicines daily for a long time. CBS coaching emphasizes the value of discipline and patience. Just like building any habit, taking your statin regularly is a step towards protecting your heart and future.
Remember, missing doses or stopping medication without your doctor’s advice can be dangerous. Regular check-ups help monitor how well the statin is working and ensure your safety.
Real-World Examples: Success Stories with Statin Therapy
Millions worldwide have seen benefits with statins. For example, people with a family history of heart disease often start statins early and reduce their risk significantly. When combined with healthy lifestyle choices, statins provide a powerful shield against heart problems.
CBS Coaching Touch: Discipline and Patience for Lasting Health Gains
Following your medication plan consistently requires a mindset similar to building a successful business or career. The principles of CBS Style—**calm mind, disciplined action, and continuous effort—**apply strongly here. Commit to your heart health with the same energy and persistence you would bring to any important life goal.
In summary, statins are the cornerstone of cholesterol medication because of their proven effectiveness and safety. They work by reducing LDL cholesterol and protecting your heart. Understanding their benefits, managing side effects, and following your doctor’s advice will help you build a strong foundation for lifelong heart health.
Ezetimibe and PCSK9 Inhibitors – Advanced Options for Better Control
While statins are very effective for many people, there are cases when lowering cholesterol requires additional treatment. Two important types of advanced cholesterol medications are Ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors. They work in different ways from statins and offer extra help to manage high cholesterol more aggressively.
What is Ezetimibe and How Does It Work?
Ezetimibe (brand name Zetia) is a medication that lowers cholesterol by blocking its absorption from the food you eat. Instead of reducing cholesterol production like statins, Ezetimibe stops cholesterol from entering your bloodstream from your intestines.
When taken alone or combined with statins, Ezetimibe can reduce LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels more effectively than statins alone. This makes it a good option for people who:
Do not reach cholesterol targets with statins alone
Cannot take high doses of statins due to side effects
Have genetic conditions causing high cholesterol
Ezetimibe is taken as a daily pill and is generally well-tolerated with few side effects.
How Effective is Ezetimibe?
Studies show that Ezetimibe can reduce LDL cholesterol by an additional 15-20% when used along with statins. This further lowering is crucial for people at high risk of heart disease.
In addition, adding Ezetimibe has been linked to lowering the risk of heart attacks and the need for heart procedures in high-risk patients.
What Are PCSK9 Inhibitors?
PCSK9 inhibitors are a newer class of cholesterol-lowering drugs. Unlike pills, these medicines are given as injections, usually once every two to four weeks.
The common PCSK9 inhibitors are:
Alirocumab (Praluent)
Evolocumab (Repatha)
These drugs help the liver remove LDL cholesterol more effectively by blocking a protein called PCSK9, which normally reduces the number of LDL receptors in the liver. When PCSK9 is blocked, more receptors are available to clear bad cholesterol from the blood.
Who Should Consider PCSK9 Inhibitors?
PCSK9 inhibitors are often prescribed for people who:
Have very high cholesterol despite using statins and Ezetimibe
Have familial hypercholesterolemia (a genetic condition causing very high LDL cholesterol)
Have heart disease and need aggressive cholesterol reduction
Cannot tolerate statins or other cholesterol medicines
Benefits of PCSK9 Inhibitors
They can reduce LDL cholesterol by 50% or more.
They significantly lower the risk of heart attack, stroke, and the need for heart procedures.
Trials show they are safe and well-tolerated by most patients.
Because PCSK9 inhibitors are relatively new and can be expensive, their use is usually reserved for people who need strong cholesterol lowering beyond what other medicines can provide.
Side Effects and Safety
Both Ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors are generally safe. Side effects are usually mild and may include:
Ezetimibe: stomach discomfort or muscle pain (rare)
PCSK9 inhibitors: injection site reactions like redness or swelling, cold symptoms
Your doctor will monitor you closely to ensure these medications are working well with minimal problems.
Combining Advanced Medications with Lifestyle
Even with powerful medicines like Ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors, lifestyle changes remain essential. Eating heart-healthy foods, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and managing stress complement the effects of medication and boost heart health.
Summary
Ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors offer excellent options for people needing extra help controlling cholesterol beyond statins. They work through different methods to safely lower LDL cholesterol and help prevent heart problems.
If your doctor prescribes these, follow their advice closely, attend regular check-ups, and maintain a healthy lifestyle for the best results.
Bile Acid Sequestrants and Other Cholesterol Medications
In addition to statins, Ezetimibe, and PCSK9 inhibitors, there are other cholesterol medications that doctors sometimes prescribe. These medicines use different methods to lower cholesterol or manage other types of fats in the blood. Understanding these options helps you and your healthcare provider choose the best treatment plan for your needs.
What Are Bile Acid Sequestrants?
Bile acid sequestrants, also known as bile acid resins, reduce cholesterol by acting in the intestines. They bind to bile acids—substances made from cholesterol that help digest fats—and remove them from your body through stool.
When bile acids are removed, your liver must use cholesterol from your blood to make more bile acids. This process reduces the level of cholesterol circulating in your body.
Common Bile Acid Sequestrants
The most commonly prescribed bile acid sequestrants include:
Cholestyramine (Questran)
Colestipol (Colestid)
Colesevelam (Welchol)
These medicines come as powders mixed with liquids or pills and are usually taken several times a day.
Effectiveness and Uses
Bile acid sequestrants can lower LDL cholesterol by about 15-25%. They are generally less powerful than statins, so they are often used:
In combination with statins or other medications
For patients who cannot tolerate statins well
For people who need additional cholesterol lowering
Side Effects and Considerations
Possible side effects of bile acid sequestrants include:
Constipation
Bloating or gas
Stomach discomfort
Because these medications bind to substances in the intestines, they may also interfere with the absorption of some vitamins and other medicines. Doctors usually recommend taking other medications at different times to avoid this problem.
Fibrates: Managing Triglycerides and More
Fibrates are a group of medications mainly used to lower triglycerides—a type of fat in the blood that can contribute to heart disease.
Common fibrates include:
Fenofibrate (Tricor)
Gemfibrozil (Lopid)
Fibrates can also raise HDL cholesterol (“good cholesterol”) but are less effective at lowering LDL cholesterol compared to statins.
Niacin (Vitamin B3)
Niacin is a vitamin that, in high doses, can lower LDL cholesterol and triglycerides and increase HDL cholesterol. However, its use has declined because of side effects like:
Flushing
Itching
Potential liver problems
Niacin is now less commonly prescribed, but it may be used in certain cases under close medical supervision.
Personalizing Cholesterol Medication
Not everyone needs these additional medicines. Your doctor will consider your cholesterol levels, health conditions, and medication tolerance to choose the best drug or combination for you. Managing cholesterol is often a personalized process.
Importance of Working Closely with Your Doctor
Because different medicines work in different ways and have varied effects, it’s important to have regular check-ups and blood tests. Your healthcare provider can monitor your cholesterol, check for side effects, and make adjustments as needed.
Summary
Bile acid sequestrants, fibrates, and niacin offer additional tools for managing cholesterol and triglycerides. While they may be less commonly used than statins or newer medicines, they still play valuable roles for specific patients.
A tailored treatment plan combining the right medications and healthy lifestyle habits gives you the best chance at controlling cholesterol and protecting your heart.
Holistic Cholesterol Management – Lifestyle, Mindset, and Long-Term Care
Managing cholesterol effectively requires more than medication alone. A healthy lifestyle and positive habits play a key role in protecting your heart and maintaining balanced cholesterol levels. This final section focuses on how you can combine medicines with lifestyle changes and the right mindset for lasting heart health.
Why Lifestyle Matters Alongside Medication
Medications help lower harmful cholesterol, but their effects are strongest when combined with healthy habits. Lifestyle changes can:
Lower cholesterol naturally
Boost the effects of medicines
Reduce other heart disease risks like high blood pressure and diabetes
Improve your overall well-being and energy
Key Lifestyle Habits for Healthy Cholesterol
1. Eat Heart-Healthy Foods
Focus on a balanced diet rich in:
Fruits and vegetables
Whole grains like oats, brown rice, and barley
Lean proteins such as fish, chicken, beans, and nuts
Healthy fats from olive oil, avocados, and fatty fish like salmon
Limit:
Saturated fats found in butter, cheese, and fatty meats
Trans fats in fried and processed foods
Excess sugar and salt
Eating well can lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL (“good cholesterol”).
2. Exercise Regularly
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise, such as:
Brisk walking
Swimming
Cycling
Dancing
Exercise helps raise HDL cholesterol, lowers LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, and strengthens your heart and blood vessels.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Losing even a small amount of weight if you are overweight can improve cholesterol levels and reduce heart disease risk.
4. Avoid Smoking
Smoking damages blood vessels and lowers good cholesterol. Quitting smoking improves your cholesterol profile and overall heart health.
5. Limit Alcohol Intake
Drinking too much alcohol can raise cholesterol and blood pressure. Stick to moderate amounts if you drink:
Up to one drink daily for women
Up to two drinks daily for men
The Role of Mindset and Stress Management
Stress can raise cholesterol and blood pressure over time. Managing stress with deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or hobbies supports heart health.
A positive mindset encourages you to stick to your lifestyle and medication plan, even when challenges arise.
Regular Monitoring and Doctor Visits
Keep regular appointments and blood tests to track your cholesterol levels and heart health. Working closely with your doctor helps adjust medicines and lifestyle advice as needed.
Summary: A Complete Approach to Heart Health
Cholesterol management is about balance—combining the power of modern medicines with natural lifestyle actions. Eating healthily, staying active, managing stress, and avoiding harmful habits improve the effectiveness of your treatment and protect your heart.
By making these changes and following your doctor’s advice, you build a strong foundation for long-term heart health.
Final Note: Your Heart Health is in Your Hands
Taking care of your cholesterol is a lifelong journey. It requires knowledge, commitment, and often a combination of medicines and good habits. But every step you take today is an investment in a healthier, longer life. Embrace this journey with care and determination to give your heart the best chance to thrive.










