Namaste! I, Guruji Sunil Chaudhary, am here to guide you through a fascinating journey into sperm formation, an essential biological process in the male reproductive system. Understanding how sperm is formed is not only crucial for medical students, doctors, and healthcare professionals but also for individuals who want to gain deeper knowledge about the human body. Sperm formation process in males.
Sperm formation, or Spermatogenesis, is a highly complex and vital function of the male reproductive system. It involves multiple biological structures, hormones, and intricate mechanisms to ensure the production of millions of sperm daily.
In this comprehensive educational guide, we will explore:
✔ Where sperm is formed
✔ How spermatogenesis works
✔ The role of hormones in sperm production
✔ How sperm fertilizes an egg
✔ Factors affecting sperm health
Let’s begin this detailed exploration of male fertility, reproductive health, and the science behind sperm formation.
Where is Sperm Formed?
One of the most frequently asked questions is “Where is sperm formed in the body?”
The answer is simple yet intricate – Sperm is formed inside the male reproductive organs called “Testes” (Testicles).
1. The Role of Testes in Sperm Formation
- Testes are two oval-shaped glands located inside a pouch-like skin structure called the Scrotum.
- These glands are responsible for producing sperm cells and testosterone, the primary male hormone.
- The temperature of the testes is 2-3 degrees Celsius lower than body temperature, which is essential for healthy sperm production.
2. Why Are the Testes Outside the Body?
Unlike other organs, the testes are located outside the body inside the scrotum. This is because:
- Sperm development requires a slightly cooler temperature than normal body heat.
- If the testes remain inside the abdomen, high temperatures could damage sperm production.
- The scrotum regulates temperature through contraction and relaxation, keeping sperm healthy and functional.
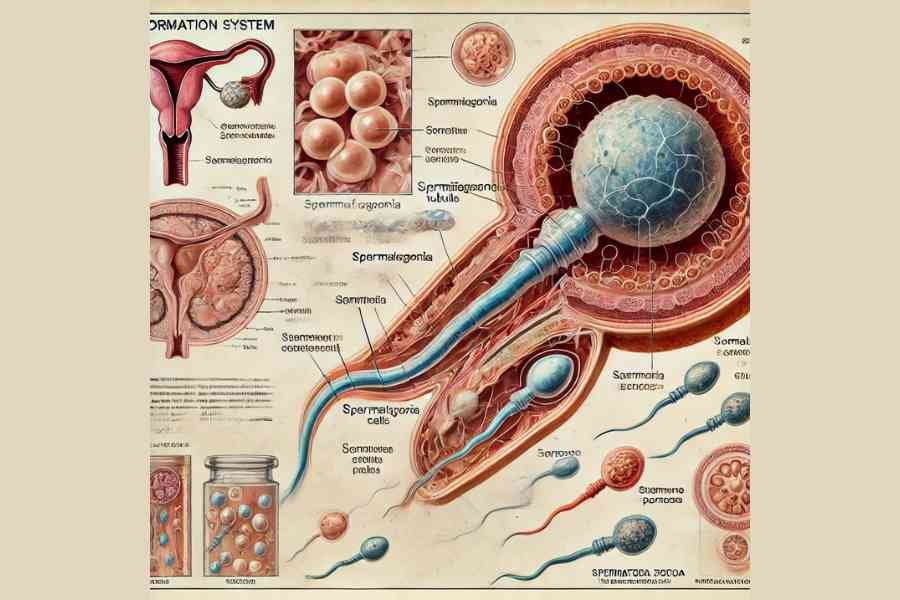
The Process of Sperm Formation – Spermatogenesis
The biological process of sperm production is called “Spermatogenesis.” It is a continuous process where millions of sperm cells are produced every day.
1. When Does Sperm Formation Start?
- A male child is born with immature reproductive organs.
- At puberty (between ages 12-14), hormone levels rise, triggering sperm production.
- The entire process takes approximately 74 days, meaning new sperm cells are constantly being formed and matured.
2. Stages of Spermatogenesis
Sperm formation happens inside tiny tubules within the testes called “Seminiferous Tubules.” These tubules contain specialized cells that divide and develop into mature sperm.
There are three main stages of sperm formation:
Stage 1: Formation of Sperm Cells (Spermatogonia to Spermatocytes)
- Special cells called Spermatogonia (stem cells) begin dividing inside the seminiferous tubules.
- These divide further into Primary Spermatocytes, which contain genetic material from the father.
Stage 2: Development into Spermatids
- Primary spermatocytes divide into Secondary Spermatocytes and then into Spermatids (immature sperm).
- At this stage, the sperm are not yet fully developed and cannot fertilize an egg.
Stage 3: Maturation into Functional Sperm (Spermatozoa)
- The immature spermatids go through a process called Spermiogenesis, where they develop:
✔ A Head (contains genetic material)
✔ A Midpiece (contains energy-producing mitochondria)
✔ A Tail (Flagellum) (helps sperm swim toward the egg) - Once mature, these sperm cells are stored in a structure called the Epididymis until ejaculation.
The Anatomy of a Sperm Cell
A mature sperm cell has a unique structure designed for movement, survival, and fertilization.
✔ Head: Contains genetic material (DNA) and is covered by an Acrosome, which helps in penetrating the female egg.
✔ Midpiece: Contains mitochondria, which provide the energy needed for sperm to move.
✔ Tail (Flagellum): Helps the sperm swim toward the egg in the female reproductive system.
How Long Does It Take for Sperm to Mature?
- The entire process of sperm formation and maturation takes 65-75 days.
- Each day, a healthy male produces around 300 million sperm.
- Once ejaculated, sperm can survive inside a female’s body for up to 48 hours.
The Role of Hormones in Sperm Production
Spermatogenesis is controlled by several hormones that regulate sperm production and male reproductive health.
✔ Testosterone: The primary male hormone responsible for sperm production and male characteristics.
✔ Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Stimulates the testes to produce sperm.
✔ Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Signals the testes to release testosterone.
How Does Sperm Fertilize an Egg?
- During sexual intercourse, sperm is released into the female reproductive tract.
- The fastest and healthiest sperm swim toward the egg inside the fallopian tube.
- The acrosome in the sperm’s head releases enzymes, allowing it to break through the egg’s outer layer.
- Once one sperm enters the egg, fertilization occurs, forming a zygote (beginning of a baby’s life).
Factors Affecting Sperm Health
Several factors can affect sperm production and quality:
✔ Healthy Diet – Zinc, Vitamin C, and antioxidants help improve sperm count.
✔ Regular Exercise – Increases testosterone levels and improves reproductive health.
✔ Avoiding Smoking & Alcohol – Reduces sperm damage and improves fertility.
✔ Lower Stress Levels – High stress can reduce sperm count.
✔ Maintaining Proper Scrotum Temperature – Avoiding excessive heat exposure (hot baths, laptops on laps) supports healthy sperm.
Final Thoughts: The Importance of Understanding Sperm Formation
✔ Spermatogenesis is a complex yet essential process for reproduction.
✔ Sperm cells are continuously produced, requiring proper health and hormonal balance.
✔ Understanding sperm formation can help in managing fertility and reproductive health.
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, understanding the role of hormones, and ensuring proper care of reproductive health, men can improve sperm quality and overall fertility.
10 Easy Daily Life tips to Keep Sperm production Healthy
Maintaining healthy sperm production is crucial for male fertility, overall health, and hormonal balance. Poor lifestyle choices, stress, and unhealthy habits can negatively impact sperm count, motility, and quality. Here are 10 easy daily life tips to naturally boost sperm health and maintain optimal reproductive function.
1. Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet 🍏🥑
A well-balanced diet plays a significant role in sperm quality and production. Include:
✔ Zinc-rich foods (Pumpkin seeds, nuts, beans) – Boosts sperm count and motility.
✔ Vitamin C & E (Citrus fruits, spinach, almonds) – Protects sperm from oxidative damage.
✔ Omega-3 fatty acids (Salmon, flaxseeds, walnuts) – Improves sperm shape and movement.
✔ Folate (Vitamin B9) (Leafy greens, lentils, avocados) – Supports sperm DNA health.
2. Stay Hydrated 💦
Drinking plenty of water helps in maintaining proper semen volume and sperm motility. Dehydration can lead to thicker semen, making it harder for sperm to move efficiently. Aim for 8-10 glasses of water daily.
3. Get Enough Sleep 😴
Lack of sleep reduces testosterone levels, affecting sperm production. Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep every night to regulate hormonal balance and improve overall reproductive health.
4. Exercise Regularly 🏋️♂️
Moderate physical activity helps maintain healthy testosterone levels and improves blood circulation to reproductive organs.
✔ Strength training – Boosts testosterone production.
✔ Cardio (running, swimming, cycling) – Enhances overall health and sperm motility.
✔ Yoga & Meditation – Reduces stress, which negatively impacts sperm count.
❌ Avoid excessive high-intensity workouts, as overtraining can reduce testosterone levels.
5. Maintain a Healthy Weight ⚖️
Being overweight or underweight can disrupt hormonal balance and lower sperm production.
✔ Obesity leads to excess estrogen production, which reduces sperm count.
✔ Maintaining a BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 supports optimal fertility.
Eating a balanced diet and staying active helps regulate hormones and sperm quality.
6. Reduce Stress & Anxiety 🧘♂️
High-stress levels increase cortisol, a hormone that suppresses testosterone production. Chronic stress can lead to:
❌ Low sperm count
❌ Poor sperm motility
❌ Erectile dysfunction
Daily meditation, deep breathing exercises, and spending time outdoors can help reduce stress and improve reproductive health.
7. Avoid Smoking & Alcohol 🚭🍺
✔ Smoking damages sperm DNA, lowers sperm count, and reduces sperm motility.
✔ Alcohol consumption decreases testosterone levels and affects sperm production.
Switch to healthier alternatives like green tea, herbal drinks, and fresh fruit juices for better hormonal balance.
8. Avoid Excessive Heat on Testes 🔥
The testicles need a cooler temperature for healthy sperm production. Avoid:
❌ Tight underwear – Wear loose, breathable cotton boxers.
❌ Hot baths & saunas – Excess heat reduces sperm count.
❌ Keeping laptops on laps – Use a table or cooling pad instead.
Keep the scrotum cool and well-ventilated to optimize sperm health.
9. Limit Exposure to Toxins & Pollutants 🚫
Toxins from plastics, pesticides, and chemicals can reduce sperm count and damage reproductive health.
✔ Use BPA-free plastic bottles and containers.
✔ Eat organic foods to avoid pesticide exposure.
✔ Reduce contact with industrial chemicals and heavy metals.
Detoxifying the body naturally with a healthy diet and regular hydration helps protect sperm health.
10. Take Essential Supplements 💊
Certain vitamins and minerals support healthy sperm production. Consider:
✔ Zinc & Selenium – Boosts sperm count and motility.
✔ Vitamin D – Increases testosterone levels.
✔ Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) – Improves sperm energy and movement.
✔ Ashwagandha & Ginseng – Natural herbs that enhance male fertility.
Before taking any supplements, consult a healthcare professional to ensure they are right for you.
Final Thoughts: Take Small Steps for Big Improvements
Maintaining sperm health is all about adopting a balanced lifestyle, eating nutritious foods, and making mindful choices. By following these simple daily habits, you can naturally boost sperm production, improve fertility, and enhance overall well-being.
✔ Eat right, stay active, and manage stress.
✔ Avoid toxins, heat exposure, and unhealthy habits.
✔ Prioritize sleep and hydration for reproductive health.
By making small daily improvements, you secure long-term reproductive health and fertility.
Call to Action
As a Digital Success Coach, my expertise is in helping individuals build thriving online businesses, automation systems, and digital marketing strategies.
📩 For expert guidance in Digital Success, Business Growth, and Automation, contact Guruji Sunil Chaudhary.
📞 Email: sunil@justbaazaar.com
🚀 Stay informed, stay educated, and always strive for success!










