Revolutionizing Lives: The UK’s ‘Artificial Pancreas’ for Type 1 Diabetes Patients
Living with type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a daily challenge that requires constant monitoring of blood sugar levels and precise insulin administration. However, a groundbreaking innovation in the UK is poised to transform the lives of those affected by T1D – the ‘artificial pancreas’. This revolutionary technology promises to bring newfound freedom and peace of mind to individuals managing this chronic condition.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This condition differs from type 2 diabetes, which is primarily influenced by lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise. In T1D, the immune system mistakenly identifies beta cells as foreign invaders and attacks them, leading to a deficiency in insulin production.
Key Points:
- Autoimmune Nature: T1D is primarily an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s immune system attacks its own cells. In the case of T1D, the immune system targets and destroys beta cells in the pancreas.
- Insulin Dependence: Since insulin is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells, individuals with T1D must rely on external insulin delivery. This can be through injections or insulin pumps.
- Blood Sugar Management: Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is paramount for individuals with T1D to prevent complications such as hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) or hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). This requires constant monitoring of blood sugar levels and adjustments to insulin doses accordingly.
- Risk of Complications: Without proper management, T1D can lead to various complications affecting organs and tissues throughout the body. These complications may include cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
- Lifestyle Factors: While lifestyle choices do not cause T1D, they can impact blood sugar control and overall health. Healthy eating, regular exercise, and stress management are essential components of managing T1D effectively.
- Ongoing Research: Researchers continue to explore various treatment options and potential cures for T1D, including artificial pancreas systems, immunotherapy, and beta cell transplantation.
Understanding the complexities of T1D is crucial for both individuals living with the condition and healthcare professionals involved in their care. It lays the foundation for effective management strategies and advancements in treatment options, such as the artificial pancreas.
The Evolution of Diabetes Management:
Advancements in medical technology have significantly transformed the landscape of diabetes management, particularly for individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D). From early innovations such as insulin pumps to the more recent development of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), these breakthroughs have empowered patients with greater control and flexibility in managing their condition.
Key Milestones:
- Insulin Pumps: Introduced in the late 1970s, insulin pumps provided an alternative to multiple daily injections by delivering insulin continuously through a small device worn on the body. This allowed for more precise insulin dosing and improved glycemic control.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): CGMs, first approved in the early 2000s, revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time monitoring of glucose levels throughout the day. By alerting users to fluctuations in blood sugar levels, CGMs enable timely interventions to prevent hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
- Integrated Insulin Pump and CGM Systems: The integration of insulin pumps with CGMs marked another milestone in diabetes management. These systems, often referred to as sensor-augmented pump therapy or hybrid closed-loop systems, allow for automated insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings, reducing the burden of manual intervention for patients.
- Artificial Pancreas: The pinnacle of diabetes technology, the artificial pancreas, represents a closed-loop system that mimics the function of the human pancreas. By combining CGM data with algorithms to adjust insulin delivery automatically, artificial pancreas systems aim to maintain stable blood sugar levels without constant user input. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize diabetes management by providing continuous, personalized care and reducing the risk of acute and long-term complications.
Future Directions:
- Improving Accuracy and Reliability: Continued research focuses on enhancing the accuracy and reliability of artificial pancreas systems to ensure safe and effective glucose control under various conditions, including during exercise and overnight.
- Expanding Accessibility: Efforts are underway to make artificial pancreas technology more accessible and affordable for a broader population of individuals with T1D, including children, adolescents, and those with varying degrees of insulin sensitivity.
- Integrating Additional Components: Future iterations of artificial pancreas systems may incorporate additional components, such as glucagon delivery to address hypoglycemia, or meal detection algorithms to optimize insulin dosing in response to carbohydrate intake.
- Pursuing Cure Therapies: While artificial pancreas technology offers significant advancements in diabetes management, ongoing research into cure therapies, such as beta cell transplantation and immunomodulatory treatments, remains crucial to ultimately eliminate the need for exogenous insulin in individuals with T1D.
The evolution of diabetes management reflects a journey of innovation and progress, driven by the collective efforts of researchers, healthcare professionals, and individuals living with diabetes. As technology continues to advance, the future holds promise for further improvements in care and the eventual realization of a cure for T1D.
The Artificial Pancreas Unveiled:
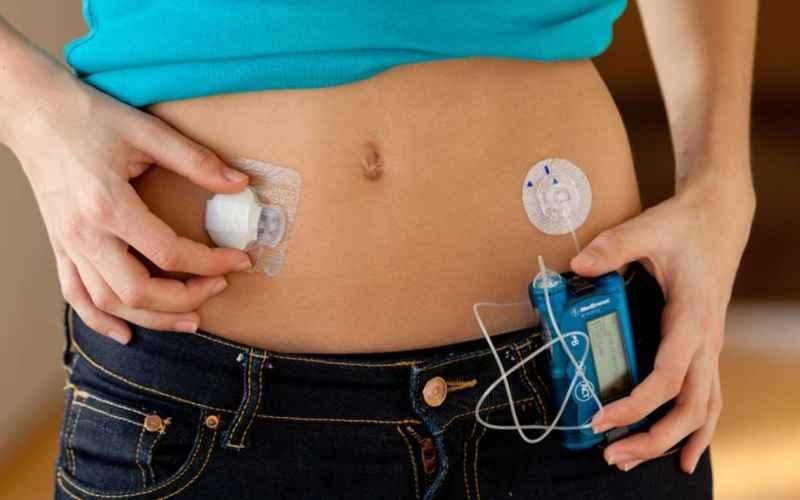
The artificial pancreas, also known as a closed-loop system, represents a groundbreaking innovation in diabetes management. This concept involves integrating insulin pumps with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and advanced algorithms to automate insulin delivery in real-time. By mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas, the artificial pancreas offers individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D) unprecedented control over their blood sugar levels while reducing the burden of manual intervention.
Key Components and Functionality:
- Insulin Pumps: Insulin pumps are small devices worn externally that deliver insulin continuously or in pre-programmed doses throughout the day. These pumps are a key component of the artificial pancreas, providing the means for insulin delivery.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): CGMs continuously monitor glucose levels in interstitial fluid, providing real-time data on blood sugar trends. This information is crucial for the closed-loop system to make informed decisions about insulin dosing.
- Sophisticated Algorithms: Advanced algorithms analyze CGM data and calculate insulin dosing requirements based on factors such as current glucose levels, rate of change, and individual insulin sensitivity. These algorithms ensure precise and timely adjustments to insulin delivery to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
- Real-time Automation: The closed-loop system operates in real-time, constantly monitoring blood sugar levels and adjusting insulin delivery accordingly. This automation significantly reduces the need for manual blood sugar checks and insulin dosing decisions, providing individuals with T1D with greater freedom and peace of mind.
Benefits of the Artificial Pancreas:
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: By automating insulin delivery based on real-time glucose data, the artificial pancreas helps individuals with T1D achieve more stable blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
- Reduced Burden: The automation of insulin delivery relieves individuals with T1D of the constant vigilance and decision-making associated with managing their condition. This can lead to improved quality of life and reduced stress related to diabetes management.
- Enhanced Flexibility: With the artificial pancreas, individuals with T1D have greater flexibility in their daily activities, such as exercise, meals, and sleep, as the system adjusts insulin delivery dynamically in response to changing glucose levels.
- Potential for Better Long-term Outcomes: By maintaining tighter blood sugar control over time, the artificial pancreas has the potential to reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and retinopathy.
Future Directions:
- Refinement and Optimization: Ongoing research focuses on refining and optimizing artificial pancreas technology to enhance its accuracy, reliability, and user-friendliness.
- Expansion of Access: Efforts are underway to make artificial pancreas systems more accessible and affordable for a broader population of individuals with T1D, including children, adolescents, and those with varying degrees of insulin sensitivity.
- Integration of Additional Features: Future iterations of the artificial pancreas may incorporate additional features, such as glucagon delivery to address hypoglycemia or meal detection algorithms to optimize insulin dosing in response to carbohydrate intake.
- Advancements in Closed-Loop Technology: Continued advancements in closed-loop technology, including miniaturization of components and improvements in battery life, aim to further enhance the usability and effectiveness of the artificial pancreas.
The unveiling of the artificial pancreas represents a significant milestone in diabetes management, offering hope for improved quality of life and better long-term outcomes for individuals living with T1D. As technology continues to evolve, the artificial pancreas holds promise as a transformative tool in the ongoing fight against diabetes.
The UK’s Pioneering Efforts:
In recent years, the United Kingdom (UK) has positioned itself as a global leader in the development and adoption of artificial pancreas technology for diabetes management. Through collaborative initiatives involving clinicians, researchers, and industry partners, the UK has made significant strides in advancing the implementation of these innovative systems in both clinical trials and real-world settings.
Key Initiatives and Achievements:
- Research Collaborations: The UK has fostered extensive collaborations between leading academic institutions, healthcare organizations, and industry stakeholders to drive research and development in artificial pancreas technology. These partnerships have facilitated the translation of scientific discoveries into practical solutions for individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D).
- Clinical Trials: The UK has been at the forefront of conducting clinical trials to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and usability of artificial pancreas systems. These trials have involved participants from diverse demographic backgrounds and have provided valuable insights into the real-world performance of these advanced technologies.
- Real-World Implementation: Building on the success of clinical trials, the UK has actively promoted the integration of artificial pancreas technology into routine clinical practice. Healthcare providers have been trained in the use of these systems, and efforts have been made to ensure accessibility for eligible patients across various healthcare settings.
- Positive Outcomes: The pioneering efforts of the UK in adopting artificial pancreas technology have yielded promising results. Participants in clinical trials and real-world settings have reported improvements in glucose control, reduction in hypoglycemic episodes, and enhanced quality of life. These outcomes underscore the transformative impact of these advanced systems on diabetes management.
- Regulatory Support: Regulatory bodies in the UK have played a proactive role in facilitating the development and deployment of artificial pancreas technology. Regulatory approvals and guidance have provided a framework for ensuring the safety, effectiveness, and reliability of these devices, thereby instilling confidence among healthcare providers and patients alike.
Future Directions:
- Continued Innovation: The UK remains committed to driving innovation in artificial pancreas technology, with ongoing research focused on enhancing system accuracy, usability, and integration of additional functionalities.
- Expansion of Access: Efforts are underway to expand access to artificial pancreas technology to a broader population of individuals with T1D, including children, adolescents, and adults with varying insulin sensitivity and healthcare needs.
- Education and Training: Comprehensive education and training programs are being developed to equip healthcare providers with the knowledge and skills required to effectively prescribe, implement, and support artificial pancreas technology in clinical practice.
- Patient Advocacy: Patient advocacy groups and organizations play a vital role in raising awareness about the benefits of artificial pancreas technology and advocating for equitable access to these life-changing innovations.
The UK’s pioneering efforts in the development and adoption of artificial pancreas technology underscore its commitment to advancing diabetes care and improving outcomes for individuals living with T1D. By leveraging collaborative partnerships, clinical expertise, and regulatory support, the UK continues to pave the way for the widespread adoption of these transformative technologies in diabetes management.
Transforming Lives:
The advent of the artificial pancreas heralds a profound transformation in the lives of individuals living with type 1 diabetes (T1D). Beyond its technological advancements, the artificial pancreas symbolizes newfound freedom, empowerment, and the opportunity to embrace life with renewed vigor and confidence.
Liberation from Diabetes Management Burdens:
- Freedom from Constant Monitoring: With the artificial pancreas automating insulin delivery based on real-time glucose data, individuals with T1D are liberated from the relentless cycle of blood sugar checks and insulin dosing decisions. This freedom from constant monitoring alleviates the mental and emotional burden associated with managing diabetes.
- Empowerment through Automation: Automation provided by the artificial pancreas empowers individuals with T1D to take back control of their lives. By relinquishing the need for manual intervention, individuals can focus their energy on pursuing their passions, aspirations, and goals without the constraints imposed by diabetes management tasks.
Opportunities for Full Participation:
- Engagement in Physical Activities: The artificial pancreas enables individuals with T1D to engage more fully in physical activities, sports, and exercise without the fear of experiencing dangerous fluctuations in blood sugar levels. This newfound ability promotes overall health and well-being while fostering a sense of confidence and accomplishment.
- Career Pursuits and Professional Success: With the burden of diabetes management significantly reduced, individuals are empowered to pursue their career aspirations with greater determination and focus. Whether in the workplace or academia, the artificial pancreas facilitates greater productivity and achievement by minimizing disruptions caused by diabetes-related issues.
Enhancing Quality of Life:
- Improved Emotional Well-being: The relief provided by the artificial pancreas translates into improved emotional well-being and mental health for individuals with T1D. Reduced stress, anxiety, and worry about blood sugar fluctuations allow for a more balanced and fulfilling life experience.
- Enhanced Social Connections: Freed from the constraints of constant diabetes management, individuals can fully engage in social activities, gatherings, and events without feeling burdened or limited by their condition. This fosters stronger connections with family, friends, and communities, enhancing overall social support and well-being.
A Brighter Future:
The artificial pancreas represents more than just a technological breakthrough—it represents hope for a brighter future for individuals living with T1D. By offering freedom, empowerment, and the opportunity to pursue a life without limitations, the artificial pancreas transforms the lives of individuals with T1D, empowering them to embrace each day with confidence, optimism, and resilience.
Looking Ahead:
The future of diabetes management holds immense promise with the continued advancement of artificial pancreas technology. As researchers, healthcare providers, policymakers, and the diabetes community collaborate, the potential for further innovation and improvement in these systems is boundless. Looking ahead, several key areas will shape the evolution of artificial pancreas technology and its impact on individuals living with type 1 diabetes (T1D).
Ongoing Research and Development:
- Enhanced Performance: Ongoing research aims to improve the performance and accuracy of artificial pancreas systems, ensuring optimal glucose control across various situations and patient populations. This includes refining algorithms, optimizing sensor technologies, and enhancing communication between components.
- Reliability and Safety: Ensuring the reliability and safety of artificial pancreas technology remains paramount. Continued research focuses on mitigating potential risks, such as device malfunctions or inaccuracies, through rigorous testing and validation processes.
- User Experience: Efforts are underway to enhance the user experience of artificial pancreas systems, making them more intuitive, user-friendly, and seamlessly integrated into daily life. This includes simplifying device interfaces, minimizing maintenance requirements, and improving wearability and comfort.
Accessibility and Affordability:
- Widespread Adoption: As artificial pancreas technology continues to mature, efforts are being made to ensure its widespread adoption and accessibility to all individuals with T1D who can benefit from it. This includes expanding insurance coverage, reducing barriers to access, and increasing awareness among healthcare providers and patients.
- Cost Reduction: Strategies to reduce the cost of artificial pancreas systems are being pursued, including streamlining manufacturing processes, leveraging economies of scale, and exploring alternative funding models. This aims to make these life-changing technologies more affordable and accessible to a broader population.
Collaboration and Support:
- Healthcare Provider Education: Comprehensive education and training programs are essential to equip healthcare providers with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively prescribe, implement, and support artificial pancreas technology in clinical practice.
- Policy Support: Policymakers play a critical role in supporting the adoption and integration of artificial pancreas technology into healthcare systems. Advocacy efforts aim to secure regulatory approvals, reimbursement policies, and funding initiatives to facilitate broader access and adoption.
- Community Engagement: The diabetes community, including patient advocacy groups, plays a vital role in driving awareness, acceptance, and support for artificial pancreas technology. Continued collaboration and engagement foster a supportive environment for innovation and improvement in diabetes care.
Transforming Lives:
The ongoing evolution of artificial pancreas technology holds the promise of transforming countless lives for the better. By enhancing glucose control, reducing the burden of diabetes management, and empowering individuals with T1D to live fuller, more active lives, these innovative systems are poised to make a profound impact on the future of diabetes care. With continued dedication, collaboration, and support, the journey toward realizing this transformative potential continues, bringing hope and opportunity to individuals with T1D around the world.
Conclusion:
In the journey to conquer type 1 diabetes, the UK’s artificial pancreas stands as a beacon of hope and progress. By harnessing the power of innovation, collaboration, and compassion, we can rewrite the narrative of T1D and empower individuals to live life to the fullest. As we look towards the future, let us continue to champion advancements that bring us closer to a world where diabetes no longer imposes limitations, but rather inspires resilience, strength, and boundless possibilities.
Top 20 FAQs about Revolutionizing Lives: The UK’s ‘Artificial Pancreas’ for Type 1 Diabetes Patients
1. What is the artificial pancreas?
- The artificial pancreas, also known as a closed-loop system, is a revolutionary technology that integrates insulin pumps with continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and sophisticated algorithms to automate insulin delivery in real-time for individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D).
2. How does the artificial pancreas work?
- The artificial pancreas constantly monitors blood sugar levels using CGMs and adjusts insulin delivery through insulin pumps based on real-time data and algorithms, mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas.
3. What are the benefits of the artificial pancreas?
- The artificial pancreas offers improved blood sugar control, reduced risk of hypoglycemia, enhanced flexibility in daily activities, and a reduced burden of diabetes management, leading to an improved quality of life for individuals with T1D.
4. Who can benefit from the artificial pancreas?
- Individuals with type 1 diabetes who require insulin therapy to manage their condition can benefit from the artificial pancreas, especially those who struggle with achieving optimal blood sugar control with traditional insulin delivery methods.
5. How does the artificial pancreas differ from traditional insulin therapy?
- Unlike traditional insulin therapy, which requires manual insulin dosing based on blood sugar measurements, the artificial pancreas automates insulin delivery based on real-time glucose data, reducing the need for constant monitoring and decision-making.
6. Is the artificial pancreas safe?
- Yes, extensive clinical trials and real-world implementations have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of artificial pancreas technology in managing blood sugar levels in individuals with type 1 diabetes.
7. How accurate is the artificial pancreas?
- The accuracy of the artificial pancreas depends on various factors, including the performance of CGMs, the reliability of insulin pumps, and the effectiveness of algorithms. Ongoing research aims to further improve the accuracy of these systems.
8. Can children use the artificial pancreas?
- Yes, artificial pancreas technology is suitable for children with type 1 diabetes, and there have been successful implementations of these systems in pediatric populations.
9. How does one access the artificial pancreas?
- Access to the artificial pancreas may vary depending on factors such as healthcare provider recommendations, insurance coverage, and availability in healthcare facilities. Individuals interested in using the artificial pancreas should consult with their healthcare team for guidance.
10. Is the artificial pancreas covered by insurance? – Insurance coverage for the artificial pancreas may vary depending on factors such as the individual’s insurance plan, regional healthcare policies, and regulatory approvals. Many insurance plans now cover artificial pancreas technology as it becomes more widely accepted and recommended by healthcare providers.
11. What are the components of the artificial pancreas system? – The artificial pancreas system typically consists of insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), and sophisticated algorithms that analyze glucose data and adjust insulin delivery accordingly.
12. Can the artificial pancreas prevent hypoglycemia? – Yes, one of the key benefits of the artificial pancreas is its ability to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia by dynamically adjusting insulin delivery based on real-time glucose trends and predictive algorithms.
13. Does the artificial pancreas require calibration? – Yes, most CGMs used in artificial pancreas systems require periodic calibration with fingerstick blood glucose measurements to ensure accuracy. However, advancements in sensor technology aim to minimize the need for frequent calibration.
14. How does exercise affect the artificial pancreas? – Exercise can impact blood sugar levels, and the artificial pancreas adjusts insulin delivery accordingly to maintain stable glucose levels during physical activity. Individuals using the artificial pancreas may need to make adjustments to their insulin settings before, during, or after exercise.
15. Can individuals with type 2 diabetes use the artificial pancreas? – While the primary focus of artificial pancreas technology has been on individuals with type 1 diabetes, there is growing interest in exploring its potential application in certain populations of individuals with type 2 diabetes who require insulin therapy.
16. How does the artificial pancreas impact quality of life? – The artificial pancreas can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with type 1 diabetes by reducing the burden of diabetes management, minimizing the risk of complications, and providing greater flexibility in daily activities.
17. What are the long-term effects of using the artificial pancreas? – Long-term studies on the effects of artificial pancreas technology are ongoing, but initial findings suggest that it can lead to improved glycemic control, reduced risk of hypoglycemia, and enhanced overall well-being for individuals with type 1 diabetes.
18. Can the artificial pancreas be used during pregnancy? – Yes, the artificial pancreas has been successfully used during pregnancy to help manage blood sugar levels in women with type 1 diabetes, providing greater control and stability during this critical period.
19. How can I learn more about the artificial pancreas? – Individuals interested in learning more about the artificial pancreas can consult with their healthcare provider, participate in educational seminars or webinars, and explore reputable online resources provided by diabetes organizations and advocacy groups.
20. What does the future hold for artificial pancreas technology? – The future of artificial pancreas technology holds promise for further advancements in performance, reliability, and accessibility. Ongoing research aims to refine algorithms, improve sensor technologies, and expand the use of these systems to benefit more individuals with type 1 diabetes.
Register for My Upcoming Masterclass HERE
See You in the Live Masterclass
Sunil Chaudhary stands as a preeminent global Leading digital coach, boasting a diverse clientele hailing from over 50 nations. Renowned for his prowess as an exemplary SEO expert, business automation coach, and landing page authority, Chaudhary also holds the distinction of being esteemed as the finest business coach in India. Beyond technical domains, he imparts invaluable insights into mindset, success, and life skills, thus encompassing a holistic approach to mentorship.












