Master tenses in English Language:
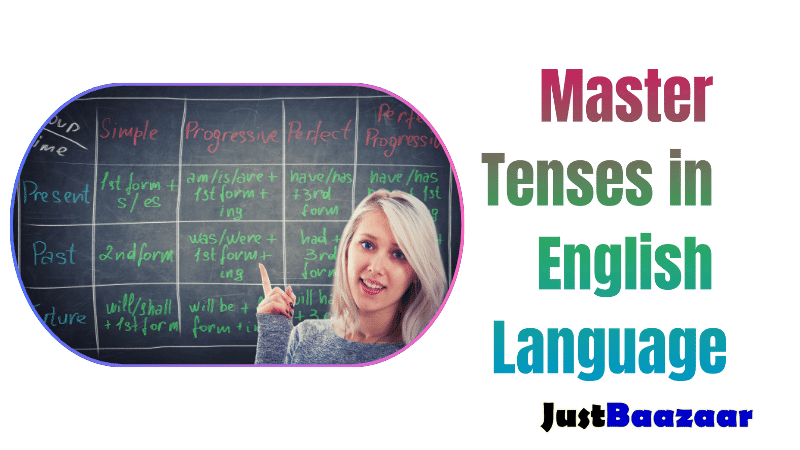
CHAPTER 1: Mastering the Basics: Understanding Verb Tenses
Introduction to Verb Tenses
In the English language, verb tenses play a crucial role in expressing time and indicating the sequence of actions or events. Understanding verb tenses is essential for effective communication, as it allows us to convey information accurately and clearly. In this chapter, we will delve into the fundamentals of verb tenses, exploring their definitions and usage in different contexts.
Present Tense: Definition and Usage
The present tense is used to describe actions or states that are happening right now or are ongoing. It gives a sense of immediacy and can be used for general statements or habitual actions. Let’s take a closer look at the different forms of present tense.
Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense is formed by using the base form of the verb. It is commonly used for facts, routines, and general truths. For example:
– “She walks to school every day.”
– “They live in Paris.”
Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is formed by using “is/are” followed by the present participle (-ing form) of the verb. It indicates an action that is happening at the moment of speaking or around this time.
– “He is playing football with his friends.”
– “I am studying for my exams.”
Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense combines “have/has” with past participle form (-ed/-en) to indicate an action that started in the past but has relevance to the present.
– “We have visited that museum before.”
– “She has already finished her work.”
Past Tense: Definition and Usage
The past tense is used to express actions or states that occurred before now. It allows us to talk about events that have already happened in a specific time frame.
Simple Past Tense
The simple past tense describes completed actions in the past without any ongoing relevance. It is formed by adding -ed to regular verbs or using the past form for irregular verbs.
– “He walked to school yesterday.”
– “They ate dinner together last night.”
Past Continuous Tense
The past continuous tense combines “was/were” with the present participle (-ing form) of the verb to indicate an ongoing action in the past at a specific moment.
– “She was studying when I called her.”
– “They were playing basketball when it started raining.”
Past Perfect Tense
The past perfect tense is formed by using “had” and the past participle of the verb. It is used to express an action that occurred before another action in the past.
– “I had already finished my work when she arrived.”
– “They had left before we got there.”
Future Tense: Definition and Usage
The future tense allows us to talk about actions or states that will happen after now. It helps us express plans, predictions, or expectations.
Simple Future Tense
The simple future tense is formed by using “will” or “shall” followed by the base form of the verb. It indicates a spontaneous decision, a promise, or a prediction about future events.
– “I will call you later.”
– “They shall arrive tomorrow.”
Future Continuous Tense
The future continuous tense uses “will be” or “shall be,” along with the present participle (-ing form) of the verb, to describe actions that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future.
– “She will be waiting for you at 8 o’clock tomorrow.”
– “We shall be traveling during summer vacation.”
Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense expresses an action that will be completed before another point in time in the future. It is formed by combining ‘will have’ with a past participle verb form.
-“By next Monday, I will have finished writing the report.”
In this chapter, we have explored the basics of verb tenses. Understanding the various verb tenses is crucial for effective communication and expressing ideas accurately. By mastering the fundamental concepts of verb tenses, you will be well-equipped to express yourself fluently in English. In the following chapters, we will delve deeper into each tense, uncovering their nuances and exploring advanced usage.
Stay tuned as we unlock the power of present tense in Chapter 2: “The Power of Present Tense: Expressing Current Actions and States.”
Chapter 2 – The Power of Present Tense: Expressing Current Actions and States
Introduction:
In the previous chapter, we explored the different verb tenses and their basic definitions. Now, it’s time to delve deeper into the present tense. The present tense allows us to express actions and states that are happening right now or are ongoing. Understanding the various forms of present tense will greatly enhance your ability to communicate effectively in English.
Overview of Present Tense Forms:
Before we dive into specific forms of present tense, let’s take a moment to understand the overall structure. Unlike other tenses, which often require auxiliary verbs or changes in verb endings, the present tense is relatively straightforward. In its simplest form, it only requires the base form of the verb.
Simple Present Tense:
The simple present tense is used to describe habitual actions or general truths. It is formed by using the base form of the verb with no added auxiliary verbs or endings. For example:
– I eat breakfast every morning.
– She speaks fluent French.
– The sun rises in the east.
This form allows us to express actions that occur regularly or facts that hold true at all times.
Present Continuous Tense:
The present continuous tense is used to express actions that are happening at this very moment or ongoing actions in progress. It is formed by using a conjugated form of “to be” (am, is, are) followed by a verb ending in -ing. For example:
– He is playing football with his friends.
– They are studying for their exams.
– We are watching a movie tonight.
This form allows us to describe temporary situations or activities happening right now.
Present Perfect Tense:
The present perfect tense combines elements of both past and present by expressing an action that started in the past but has an impact on the present. It is formed by using “have” or “has” as auxiliary verbs followed by a past participle. For example:
– I have visited Paris several times.
– She has already finished her work.
– We have lived in this city for five years.
This form allows us to discuss experiences or actions that have a connection to the present moment.
Connecting Present Tense Forms:
The ability to switch between different forms of the present tense adds depth and nuance to your language skills. By using the simple present tense, you can express general truths or habits. When you want to highlight ongoing actions, the present continuous tense is appropriate. Finally, if you need to convey an action with relevance to the current time, the present perfect tense is your go-to choice.
By mastering these forms of the present tense, you will be able to communicate effectively and accurately in various situations. Whether it’s describing your daily routine, discussing temporary situations, or sharing past experiences with a connection to the present, these tenses will become invaluable tools in your English language repertoire.
Conclusion:
In this chapter, we explored the power of the present tense in expressing current actions and states. We learned about its different forms – simple present tense for habitual actions and general truths, present continuous tense for ongoing actions, and present perfect tense for actions with a connection to the current time. By understanding and utilizing these forms effectively, you can enhance your communication skills in English.
In our next chapter, “Journey into the Past: Reliving Past Events through Verb Tenses,” we will explore how verb tenses can help us discuss events that have already happened. Stay tuned as we embark on an exciting journey through time!
Chapter 3 – Journey into the Past: Reliving Past Events through Verb Tenses
Introduction:
In the previous chapters, we explored the basics of verb tenses and delved into the power of expressing current actions and states with present tense. Now, it’s time to embark on a journey into the past. Understanding how to effectively use past tense forms will allow you to relive past events and communicate with clarity and accuracy. In this chapter, we will explore the various past tense forms, from simple past to past continuous and past perfect.
Overview of Past Tense Forms:
Before diving into specific forms, let’s have an overview of the different ways in which we can express actions or events that occurred in the past. The three main forms of expressing past tense are simple past, past continuous, and past perfect.
1. Simple Past Tense:
The simple past tense is used to describe completed actions or states that happened at a specific time in the past. It is formed by adding “-ed” to regular verbs or using irregular verb forms.
For example:
– I walked to school yesterday.
– She ate dinner at a fancy restaurant last night.
– They played soccer every weekend when they were young.
2. Past Continuous Tense:
The past continuous tense is used to describe ongoing actions or states that were happening in the past at a specific moment or during a certain period of time. It is formed by using “was” or “were” as auxiliary verbs followed by the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
For example:
– I was reading a book when he called me.
– They were studying for their exams all night long.
– She was dancing gracefully on stage while everyone applauded.
3. Past Perfect Tense:
The past perfect tense is used when we want to express an action or state that occurred before another action in the past. It helps us establish a clear sequence of events. It is formed by using “had” as an auxiliary verb followed by the past participle of the main verb.
For example:
– He had already finished his homework before his friends arrived.
– We had visited that museum several times before it closed down.
– By the time she reached the party, everyone had left.
Simple Past Tense: Formation and Examples:
The simple past tense is perhaps one of the most commonly used past tense forms in English. It is straightforward to form for regular verbs by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb. However, irregular verbs have unique forms that must be memorized.
Regular Verbs:
To form the simple past tense for regular verbs, simply add “-ed” to the base form of the verb.
For example:
– Walk (base form) becomes walked (simple past).
– Talk (base form) becomes talked (simple past).
– Play (base form) becomes played (simple past).
Irregular Verbs:
Irregular verbs do not follow a specific pattern when forming their simple past tense. Each verb has its own unique form that must be learned individually.
For example:
– Go (base form) becomes went (simple past).
– Eat (base form) becomes ate (simple past).
– See (base form) becomes saw (simple past).
Past Continuous Tense: Formation and Examples:
The past continuous tense allows us to describe actions or states that were happening at a specific moment or during a certain period in the past.
Formation:
The formula for forming the past continuous tense is as follows: subject + was/were + present participle (-ing).
For example:
– I was studying when my friend called.
– They were playing video games all night long.
– She was cooking dinner while listening to music.
Past Perfect Tense: Formation and Examples:
The past perfect tense helps us establish a clear sequence of events by expressing an action or state that occurred before another action in the past.
Formation:
The formula for forming the past perfect tense is as follows: subject + had + past participle.
For example:
– He had already left before I arrived.
– They had finished their work by the time I woke up.
– She had traveled to many countries before settling down.
Conclusion:
Mastering the various forms of past tense allows us to effectively communicate about events and actions that have occurred in the past. By using simple past, past continuous, and past perfect tenses appropriately, we can provide a clear timeline of events and create engaging narratives. Understanding these tenses is crucial for anyone looking to express themselves accurately in English. So, continue practicing and integrating these verb forms into your everyday language, and you will soon become a master of tenses in English Language.
Chapter 4: Embracing the Future Ahead: Anticipating What’s to Come with Verb Tenses
Introduction:
In this chapter, we will delve into the realm of future verb tenses. Just as the present and past tenses allow us to express actions and states in the current and past moments, future tenses help us anticipate events that are yet to occur. Understanding these verb forms will empower you to confidently communicate about upcoming actions and plans. Let us explore the various forms of future tenses together.
Overview of Future Tense Forms:
Before we explore each form in detail, let’s take a step back and understand the general structure of future tense verbs. In English, we primarily use three forms when referring to future actions or states: simple future tense, future continuous tense, and future perfect tense.
Simple Future Tense:
The simple future tense is used when expressing an action that will happen at a specific time in the future. It is formed by adding “will” or “shall” before the base form of the verb. For example:
– I will complete my assignment tomorrow.
– She shall meet her friend next week.
Future Continuous Tense:
When we want to emphasize an ongoing action that will be happening in the future, we use the future continuous tense. This form is created by using “will be” or “shall be” followed by a present participle (-ing form) of the verb. Examples include:
– They will be traveling around Europe next summer.
– We shall be waiting for you at the airport.
Future Perfect Tense:
The future perfect tense is employed when expressing an action that will be completed before a specific time in the future. We construct this form by using “will have” or “shall have” followed by a past participle of a verb. Take note of these examples:
– By next month, he will have finished writing his novel.
– They shall have completed the project by the end of the year.
Elaborating on Future Tense Forms:
Simple Future Tense:
The simple future tense enables us to discuss plans, predictions, and intentions for events that will occur in the future. It is a versatile form that can be used to express both certainty and uncertainty. For instance:
– We will visit our grandparents over the holidays.
– She will probably pass her driving test next week.
Future Continuous Tense:
The future continuous tense emphasizes actions or events that will be ongoing at a specific moment in the future. This form conveys a sense of continuity and duration. Consider these examples:
– They will be celebrating their anniversary at a fancy restaurant tomorrow night.
– I shall be studying all day for my upcoming exams.
Future Perfect Tense:
By using the future perfect tense, we can describe an action that will already have been completed before another event or time in the future. It highlights actions that precede other actions or states. Take a look at these examples:
– By this time next year, she will have graduated from university.
– They shall have left for their vacation before we arrive.
Connecting Material to Book Title:
Master tenses in English Language encompasses not only understanding verb tenses but also mastering their practical usage in everyday communication. By embracing future verb tenses, you are taking another step towards becoming fluent in English and expressing your thoughts about upcoming events with precision and accuracy.
Conclusion:
In this chapter, we explored three forms of future verb tenses: simple future tense, future continuous tense, and future perfect tense. Each form serves its unique purpose when discussing actions or states yet to happen. Understanding how to construct and use these forms correctly is crucial for effective communication in English language mastery. With this knowledge under your belt, you are now equipped to confidently talk about what lies ahead using appropriate verb tenses as you continue your journey through this book on mastering tenses in the English language.
Chapter 5: Perfecting Your Language Skills with Perfect Tenses
Introduction:
As we delve deeper into the world of verb tenses, it is essential to explore the realm of perfect tenses. In this chapter, we will unravel the intricacies of perfect tenses and how they can elevate your language skills to new heights. Whether it’s expressing ongoing actions or emphasizing completed events, mastering perfect tenses is crucial for effective communication in English.
Overview of Perfect Tenses:
Perfect tenses are formed by combining a form of the auxiliary verb “have” with the past participle of the main verb. These tenses allow us to convey a sense of completion or continuity in relation to a specific time frame.
1. Present Perfect Continuous:
The present perfect continuous tense demonstrates an ongoing action that started in the past, continues into the present, and may still continue in the future. It is formed by using “have been” + present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
Example:
– She has been studying all night.
– We have been waiting for hours.
This tense is particularly useful when discussing actions that have a direct impact on the present or when indicating duration or repetition.
2. Past Perfect Continuous:
The past perfect continuous tense describes an action that began in the past and continued up until another point in time in the past. It is formed by using “had been” + present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
Example:
– They had been playing tennis since morning before it started raining.
– She had been working at that company for five years before she decided to resign.
By using this tense, we can highlight actions that were ongoing and relevant at a specific moment in history before being interrupted or completed.
3. Future Perfect Continuous:
The future perfect continuous tense expresses an ongoing action that will be completed at some point in the future. It is formed by using “will have been” + present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
Example:
– By this time next year, I will have been living in this city for a decade.
– They will have been traveling for two months when they finally arrive at their destination.
This tense allows us to discuss actions that will still be in progress at a specific future point, emphasizing the duration or continuity of those actions.
Connecting Material to the Book Title:
By delving into perfect tenses, we are taking a significant step towards mastering the intricacies of English language skills. Understanding and utilizing perfect tenses enables us to express ourselves more precisely, emphasizing completion or continuity while communicating effectively.
Conclusion:
Perfect tenses provide us with a powerful toolset to convey nuanced meanings and enhance our language skills. The present perfect continuous, past perfect continuous, and future perfect continuous tenses allow us to express ongoing actions with relevance to specific time frames. By practicing and incorporating these tenses into our daily conversations and written expressions, we can elevate our mastery of English language tenses.
In the next chapter, we will explore advanced topics such as conditional sentences and reported speech. These concepts build upon our foundation of verb tenses and further enhance our ability to communicate fluently in English. So let’s continue this journey together as we strive towards becoming proficient users of English grammar and language structures.















